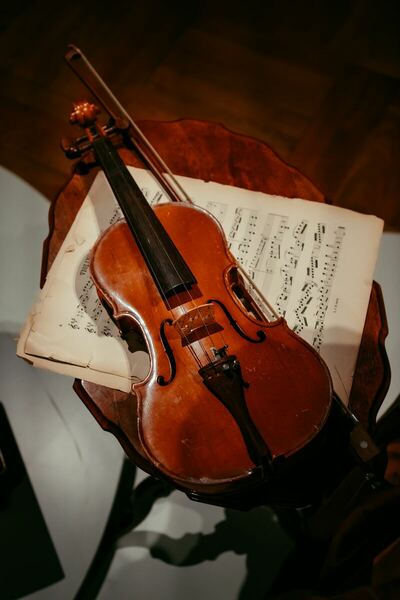

In this study the authors looked at the ability of artificial intelligence to detect tempo, rhythm, and intonation of a piece played on violin. Technology such as this would allow for students to practice and get feedback without the need of a teacher.
Read More...



.jpg)