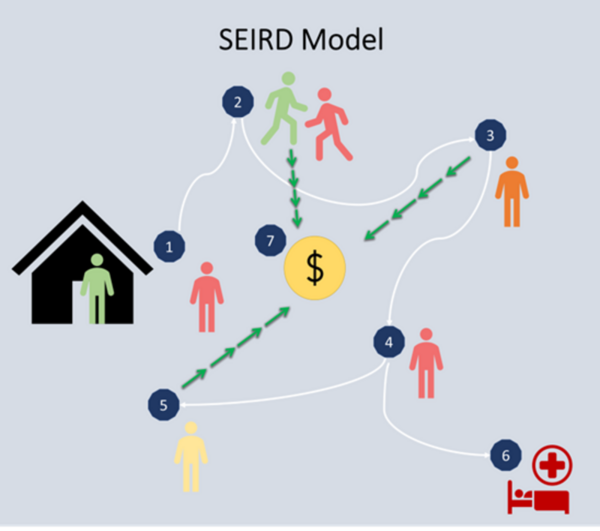
Pandemics involve the high transmission of a disease that impacts global and local health and economic patterns. Epidemiological models help propose pandemic control strategies based on non-pharmaceutical interventions such as social distancing, curfews, and lockdowns, reducing the economic impact of these restrictions. In this research, we utilized an epidemiological Susceptible, Exposed, Infected, Recovered, Deceased (SEIRD) model – a compartmental model for virtually simulating a pandemic day by day.
Read More...