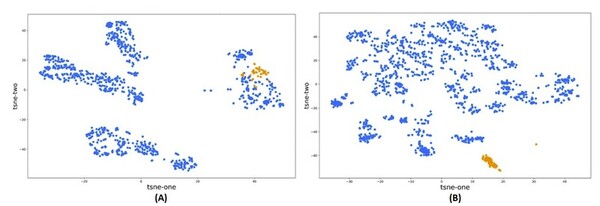
With advancements in machine learning a large data scale, high throughput virtual screening has become a more attractive method for screening drug candidates. This study compared the accuracy of molecular descriptors from two cheminformatics Mordred and PaDEL, software libraries, in characterizing the chemo-structural composition of 53 compounds from the non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTI) class. The classification model built with the filtered set of descriptors from Mordred was superior to the model using PaDEL descriptors. This approach can accelerate the identification of hit compounds and improve the efficiency of the drug discovery pipeline.
Read More...


.jpg)