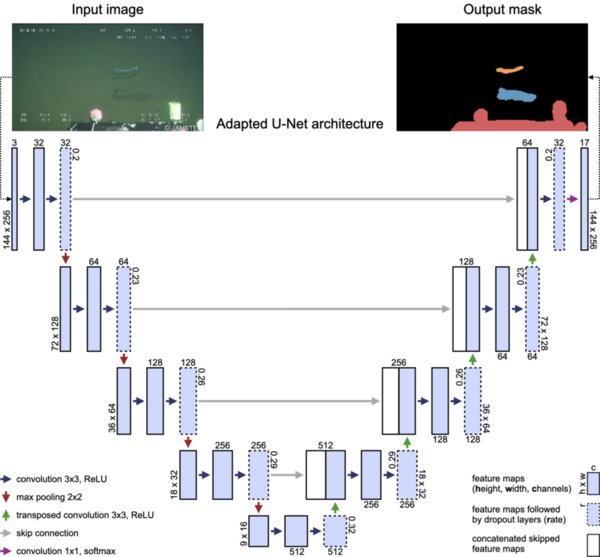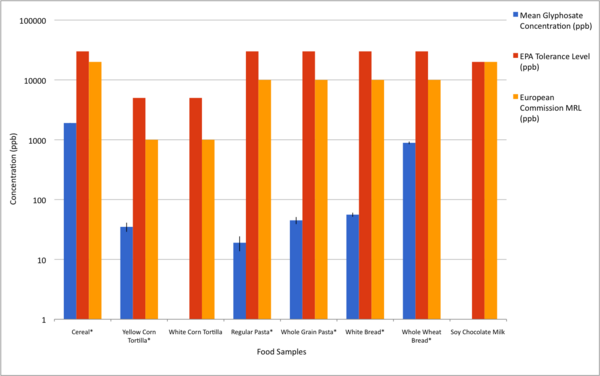
Glyphosate is the active ingredient in the herbicide Roundup, frequently used in the agricultural industry worldwide. Current literature reveals contradictory findings regarding the effects of glyphosate on vertebrates, leading to concerns about human consumption and differing views on safety levels. Here, authors sought to measure glyphosate levels in common commercially available food products. While some product levels exceed the thresholds at which negative effects have been observed, none exceed government limits.
Read More...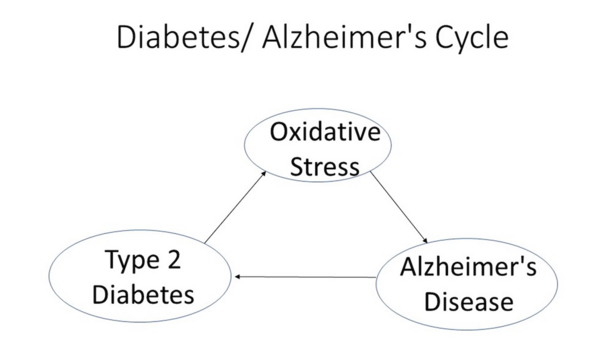
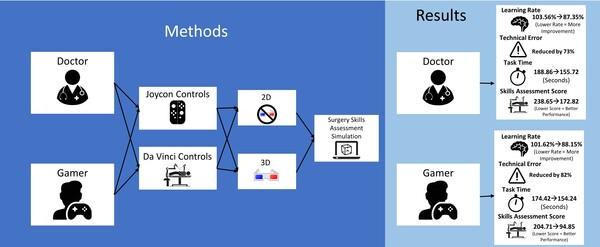

.png)