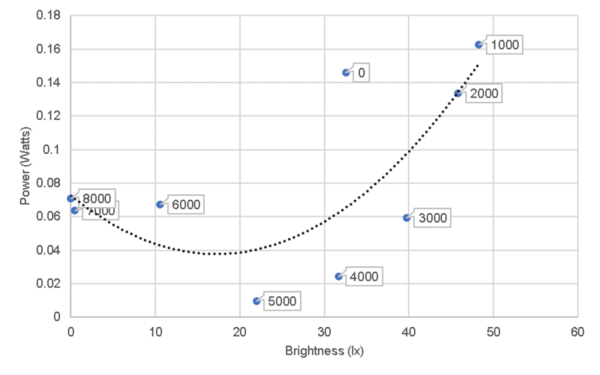
Buildings, which are responsible for the majority of electricity consumption in cities like Dubai, are often exclusively reliant on electrical lighting even in the presence of daylight to meet the illumination requirements of the building. This inefficient use of lighting creates potential to further optimize the energy efficiency of buildings by complementing natural light with electrical lighting. Prior research has mostly used ballasts (variable resistors) to regulate the brightness of bulbs. There has been limited research pertaining to the use of pulse width modulation (PWM) and the use of ‘triodes for alternating current’ (TRIACs). PWM and TRIACs rapidly stop and restart the flow of current to the bulb thus saving energy whilst maintaining a constant illumination level of a space. We conducted experiments to investigate the feasibility of using TRIACs and PWM in regulating the brightness of bulbs. We also established the relationship between power and brightness within the experimental setups. Our results indicate that lighting systems can be regulated through these alternate methods and that there is potential to save up to 16% of energy used without affecting the overall lighting of a given space. Since most energy used in buildings is still produced through fossil fuels, energy savings from lighting systems could contribute towards a lower carbon footprint. Our study provides an innovative solution to conserve light energy in buildings during daytime.
Read More...
.jpg)
.jpg)