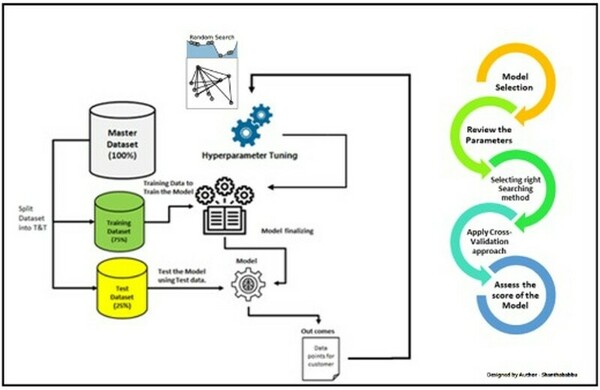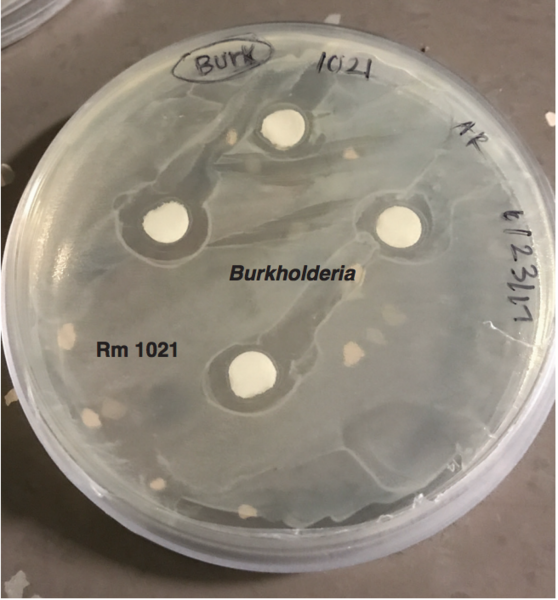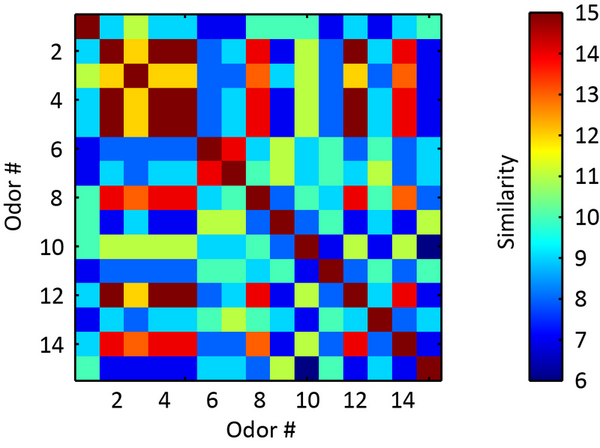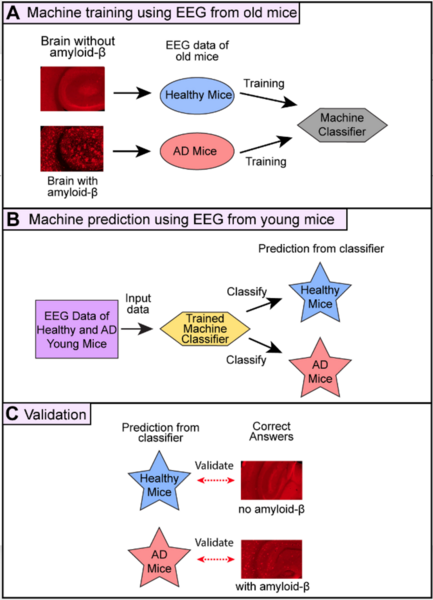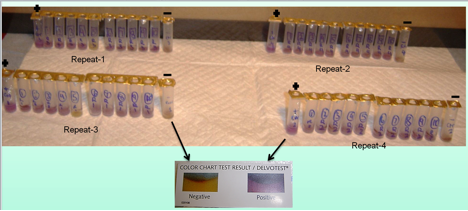
Antibiotics are oftentimes used to treat mastitis (infection of the mammary gland) in dairy cows. Regulations require that milk from these cows be discarded until the infection has cleared and antibiotic residues are no longer detectable in the cow's milk. These regulations are in place to protect consumers and to help prevent the rise of antibiotic resistant bacteria. In this study, the authors test milk samples from 10 milk suppliers in the Greensboro, NC to see if they contain detectable levels of antibiotic residues.
Read More...