The authors investigate the ability of machine learning models to developing new drug-like molecules by learning desired chemical properties versus simply generating molecules that similar to those in the training set.
Read More...Evaluating the feasibility of SMILES-based autoencoders for drug discovery

The authors investigate the ability of machine learning models to developing new drug-like molecules by learning desired chemical properties versus simply generating molecules that similar to those in the training set.
Read More...Comparative study of machine learning models for water potability prediction
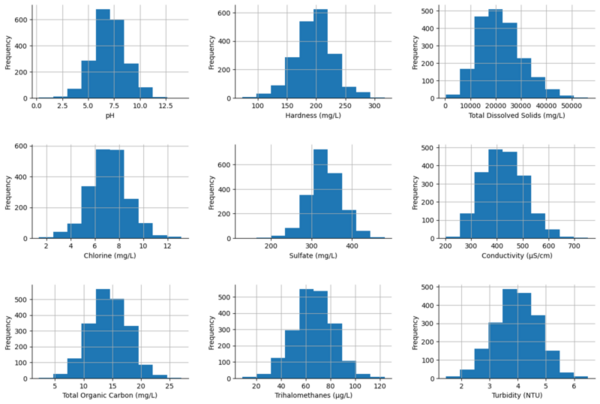
The global issue of water quality has led to the use of machine learning models, like ANN and SVM, to predict water potability. However, these models can be complex and resource-intensive. This research aimed to find a simpler, more efficient model for water quality prediction.
Read More...Applying machine learning to breast cancer diagnosis: A high school student’s exploration using R
The authors combine fine needle aspiration biopsy and machine learning algorithms to develop a breast cancer detection method suitable for resource-constrained regions that lack access to mammograms.
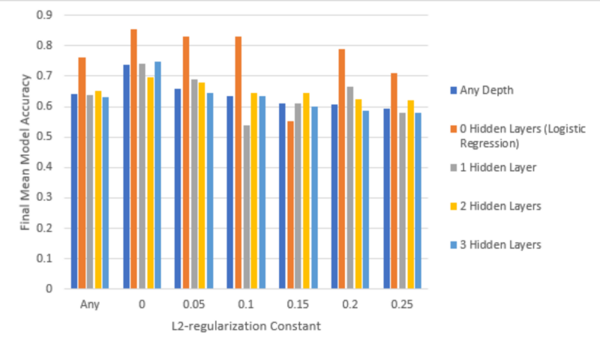
Read More...Study of neural network parameters in detecting heart disease
The authors looked at the ability to detect heart disease before the onset of severe clinical symptoms.
Read More...A HOG feature extraction and CNN approach to Parkinson’s spiral drawing diagnosis

Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a prevalent neurodegenerative disorder in the U.S., second only to Alzheimer’s disease. Current diagnostic methods are often inefficient and dependent on clinical exams. This study explored using machine and deep learning to enhance PD diagnosis by analyzing spiral drawings affected by hand tremors, a common PD symptom.
Read More...Evaluating the clinical applicability of neural networks for meningioma tumor segmentation on 3D MRI
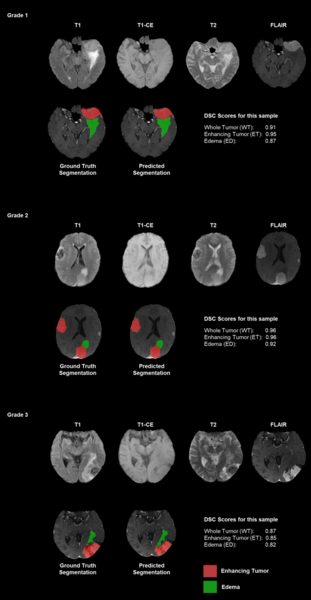
Authors emphasize the challenges of manual tumor segmentation and the potential of deep learning models to enhance accuracy by automatically analyzing MRI scans.
Read More...The effects of regeneration on memory in planarians
The authors test the ability of planarians to remember conditioned stimuli following regeneration.
Read More...Teenagers’ memory recall of narrative writing versus informational writing and its link to emotion

Here, seeking to understand the effects of emotion on memory recall, the authors used a study of 30 teenagers, comparing their ability to recall details from information or narrative writing. They found improved recall of narrative writing, suggesting emotional response can contribute to improved memory recall.
Read More...Can the nucleotide content of a DNA sequence predict the sequence accessibility?

Sequence accessibility is an important factor affecting gene expression. Sequence accessibility or openness impacts the likelihood that a gene is transcribed and translated into a protein and performs functions and manifests traits. There are many potential factors that affect the accessibility of a gene. In this study, our hypothesis was that the content of nucleotides in a genetic sequence predicts its accessibility. Using a machine learning linear regression model, we studied the relationship between nucleotide content and accessibility.
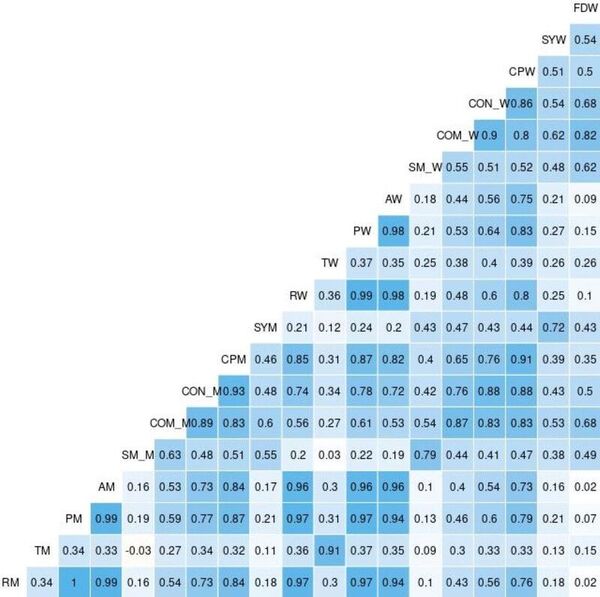
Read More...Analyzing the Relationships Between Internet Usage, Social Skill, and Anxiety Severity in Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder
.jpg)
Here the authors investigate the use of social media in adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in affecting their ability and opportunities to interact with others. They found that higher usage of Internet correlated with less severe anxiety symptoms and improved social skills.
Read More...