Machine learning for retinopathy prediction: Unveiling the importance of age and HbA1c with XGBoost
(1) Mallya Aditi International School, (2) Shri B. M. Patil Medical College, Hospital and Research Center
https://doi.org/10.59720/23-184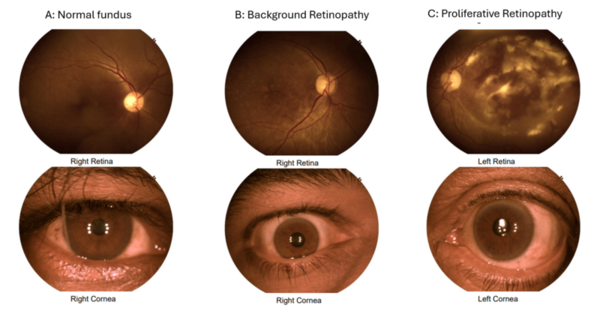
Retinopathy is a major microvascular complication of both diabetes and hypertension. It can lead to blindness if left untreated. As one in three adults in India is estimated to be either diabetic or hypertensive, their future risk of developing retinopathy is high. The purpose of our study was to examine the correlation of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), blood pressure (BP) readings, and lipid levels with retinopathy. Our main hypothesis was that poor glycemic control, as evident by high HbA1c levels, high blood pressure, and abnormal lipid levels, causes an increased risk of retinopathy. We screened 119 Indian patients using a Fundus camera for retinopathy and obtained their recent BP, HbA1c, and lipid profile values. We then applied the XGBoost machine learning algorithm to predict the presence or absence of retinopathy from their lab values. We were able to predict retinopathy with high accuracy from these key biomarkers. Further, using Shapely Additive Explanations (SHAP), we identified the top two features that were most important to the model as age and HbA1c. This indicates that older patients with poor glycemic control are more likely to show presence of retinopathy. Hence, these high-risk individuals can be targeted for early screening and intervention programs to prevent the progression of retinopathy to blindness.
This article has been tagged with: