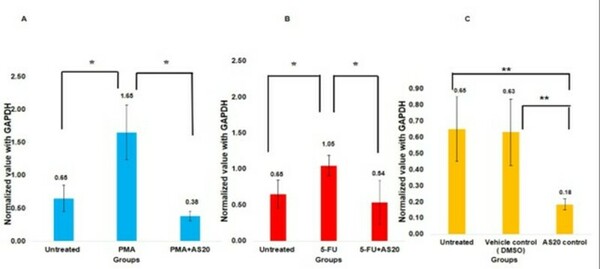
The authors found that treatment with AS20 suppressed phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and 5-flurouracil (5-FU) induction of COX2 expression. We also observed AS20 treated cells showed DNA fragmentation in HeLa cells.
Read More...Apoptosis induction and anti-inflammatory activity of polyherbal drug AS20 on cervical cancer cell lines

The authors found that treatment with AS20 suppressed phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and 5-flurouracil (5-FU) induction of COX2 expression. We also observed AS20 treated cells showed DNA fragmentation in HeLa cells.
Read More...Utilizing 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 to prevent the appearance of diabetic-like phenotypes in Drosophila melanogaster

This study aimed to assess the role of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 solution, at varying concentrations, in protecting vertical transmission of diabetic-like phenotypes. We hypothesized that the highest concentration of vitamin D solution (55 ng/mL) would be most effective in having a protective role. The results indicated that the hypothesis was partially supported; overall, all three concentrations of the vitamin D solution administered to the flies reared on HSDs had a protective effect, to varying extents.
Read More...The peroxidase-like activity of papain colorimetrically detects H2O2 and glucose with high sensitivity
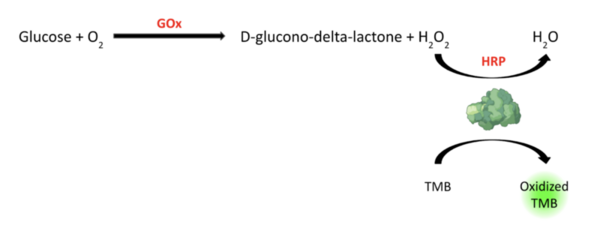
Many diabetics agree that the current glucometer methods are invasive, inefficient, and unsustainable for measuring blood glucose. These authors investigate the possibility of using a non-invasive glucometer patch that predicts blood glucose from patient sweat, with high accuracy.
Read More...Characterizing the association between hippocampal reactive astrogliosis, anhedonia-like behaviors, and neurogenesis in a monkey model of stress and antidepressant treatment
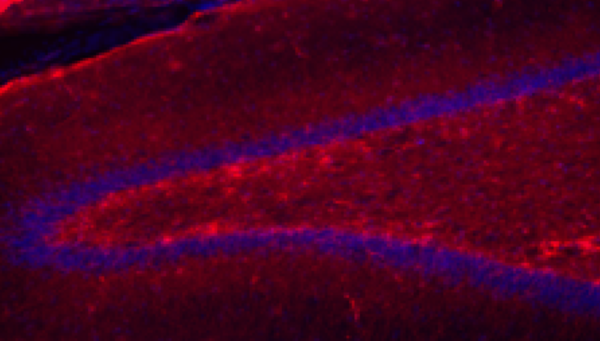
This study examined the effects of stress and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) on a measure of astrocyte reactivity in nonhuman primate (NHP) models of stress. Results showed that chronic separation stress in NHPs leads to increased signs of astrogliosis in the NHP hippocampus. The findings were consistent with the hypotheses that hippocampal astrogliosis is an important mechanism in stress-induced cognitive and behavioral deficits.
Read More...Herbal formulation, HF1 diminishes tumorigenesis: a cytokine study between MCF-7 and BM-MSCs.

The authors use HF-1, an herbal formation, on bone marrow derived cells as well as breast cancer cells to assess HF-1's ability to prevent tumorigenesis. As metastasis requires coordination of multiple cells in the tumor microenvironment, their findings that HF-1 augments cytokine expression such as VEGF & TGF-B show that HF-1 has potential application to therapeutics.
Read More...The effect of sports on teenagers’ depression symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic

Here, seeking to identify the possible role of sports in helping teenagers navigate the troubles associated with societal changes during a pandemic, the authors surveyed 50 adolescents to collect Beck Depression Inventory scores. They found that 9 out of students with severe depressions did not do sports, while no significant relationship between depressive symptoms and either gender or place of exercise was observed.
Read More...Antibacterial Effects of Copper Surfaces
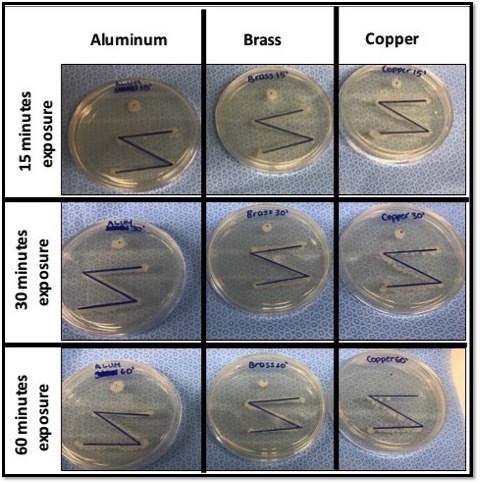
This study examined the ability of copper and copper alloy surfaces to inhibit bacterial growth, which may be help prevent healthcare-associated infections. The authors exposed two non-pathogenic strains of bacteria to different metal plates for varying degrees of time and measured bacterial growth.
Read More...Accessibility to urgent care services for disadvantaged populations: An analysis of healthcare disparities
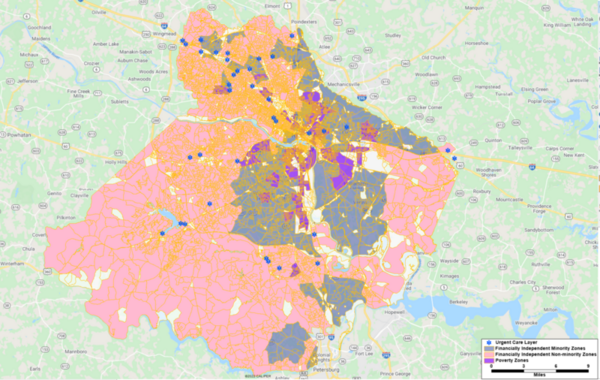
The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated the depth and significance of healthcare inequality in the United States. Xiao, Xiao, and Gong examine healthcare disparities in the Richmond (Virginia) metropolitan area by analyzing whether people from disadvantaged populations must travel for longer to reach healthcare facilities.
Read More...The juxtaposition of anatomy and physics in the eye
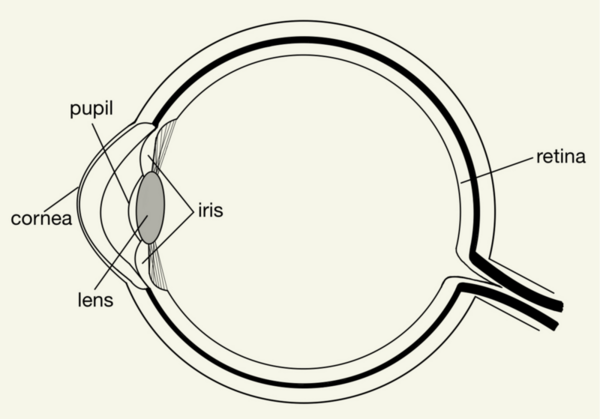
People are quick to accept the assumption that a light will appear dimmer the farther away they are, citing the inverse square relationship that illuminance obeys as rationale. However, repeated observations of light sources maintaining their brightness over large distances prompted us to explore how the brightness, or perceived illuminance of a light varies with the viewing distance from the object. We hypothesized that since both the illuminance of the light source and image size decrease at the same rate, then the concentration, or intensity of the image remains unchanged, and subsequently the perceived illuminance.
Read More...Prediction of preclinical Aβ deposit in Alzheimer’s disease mice using EEG and machine learning
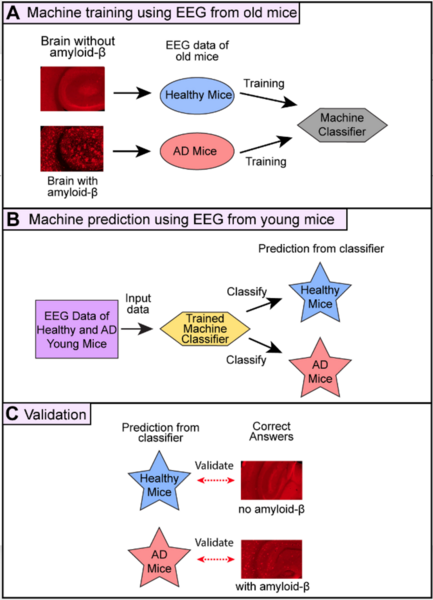
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a common disease affecting 6 million people in the U.S., but no cure exists. To create therapy for AD, it is critical to detect amyloid-β protein in the brain at the early stage of AD because the accumulation of amyloid-β over 20 years is believed to cause memory impairment. However, it is difficult to examine amyloid-β in patients’ brains. In this study, we hypothesized that we could accurately predict the presence of amyloid-β using EEG data and machine learning.
Read More...Search articles by title, author name, or tags