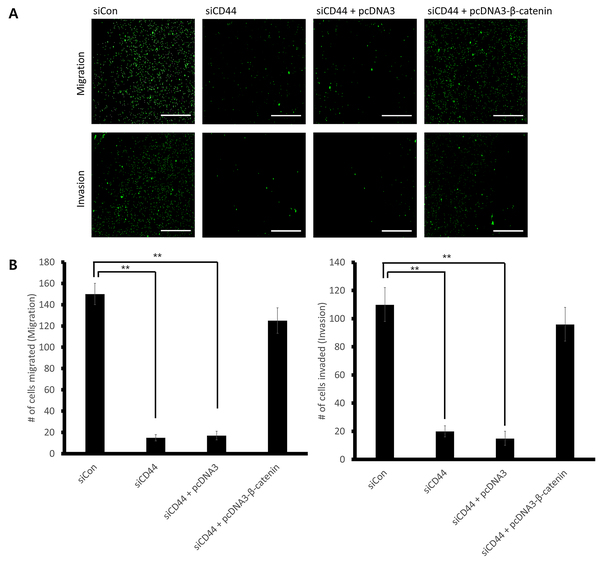
In this study, we aimed to characterize CD44-mediated regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which promotes cancer invasion and metastasis. We hypothesized that CD44 down-regulation will inhibit gastric cancer cell migration and invasion by leading to down-regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. We found that CD44 up-regulation was significantly related to poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients. We demonstrated the CD44 down-regulation decreased β-catenin protein expression level. Our results suggest that CD44 down-regulation inhibits cell migration and invasion by down-regulating β-catenin expression level.
Read More...