Down-regulation of CD44 inhibits Wnt/β-catenin mediated cancer cell migration and invasion in gastric cancer
(1) The Hudson School, Hoboken, NJ, (2) Department of Biological Science, University of Suwon, Wau-ri, Bongdam-eup, Hwaseong, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea
https://doi.org/10.59720/20-090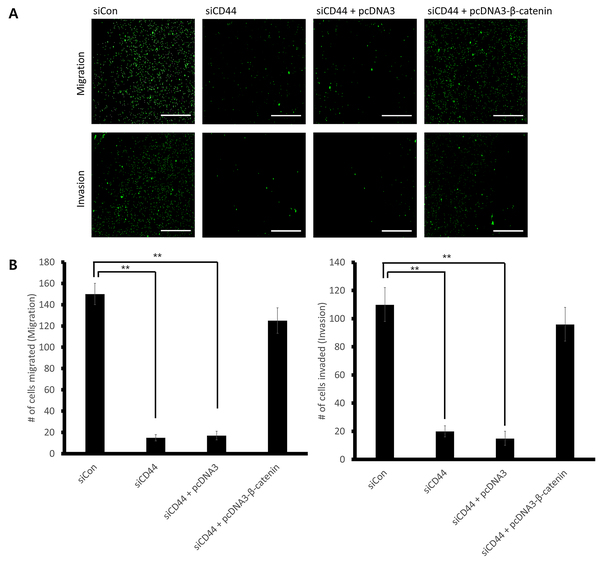
Recent studies tried to find the genes that are associated with gastric cancer patient’s survival. Many studies focused on CD44, which is associated with gastric cancer tumorigenesis and metastasis. However, the mechanisms by which molecules downstream of CD44 contribute to gastric cancer cell migration and invasion remain poorly studied. The lack of information on CD44 downstream mechanism limits the development of effective therapies for patients with gastric cancer. In this study, we aimed to characterize CD44-mediated regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which promotes cancer invasion and metastasis. We hypothesized that CD44 down-regulation will inhibit gastric cancer cell migration and invasion by leading to down-regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. We found that CD44 up-regulation was significantly related to poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients. We demonstrated the CD44 down-regulation decreased β-catenin protein expression level. Our results suggest that CD44 down-regulation inhibits cell migration and invasion by down-regulating β-catenin expression level. We determined not only that CD44 regulates the expression level of β-catenin, but also discovered a novel CD44/β-catenin pathway that regulates cell migration and invasion in gastric cancer. Our findings suggest that targeting the CD44/β-catenin pathway may be an effective therapeutic strategy for gastric cancer patients.
This article has been tagged with: