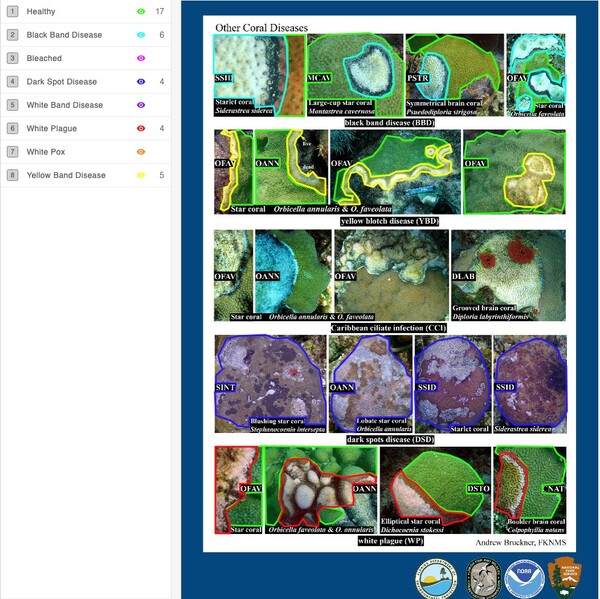
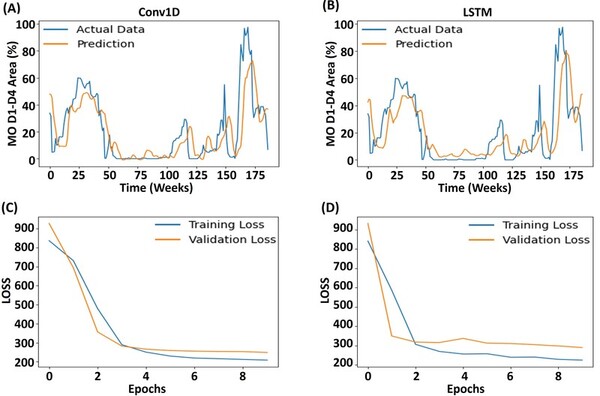
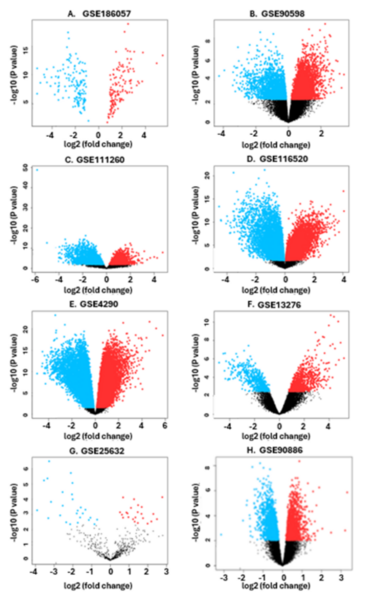
Here the authors sought to understand the effects of different variables that may be tied to pollution and climate change on genetic variation of Pacific white-sided dolphins, a species that is currently threatened by water pollution. Based on environmental data collected alongside a genetic distance matrix, they found that ocean currents had the most significant impact on the genetic diversity of Pacific white-sided dolphins along the Japanese coast.
Read More...