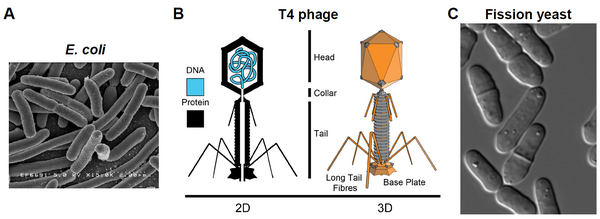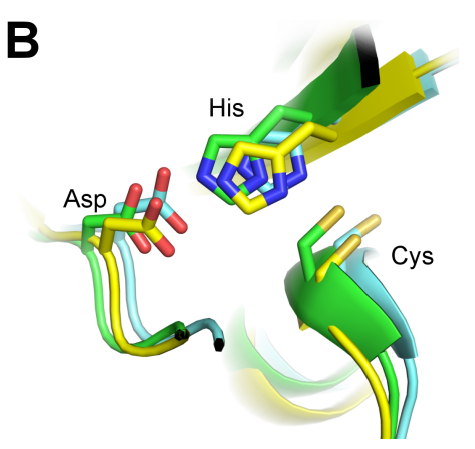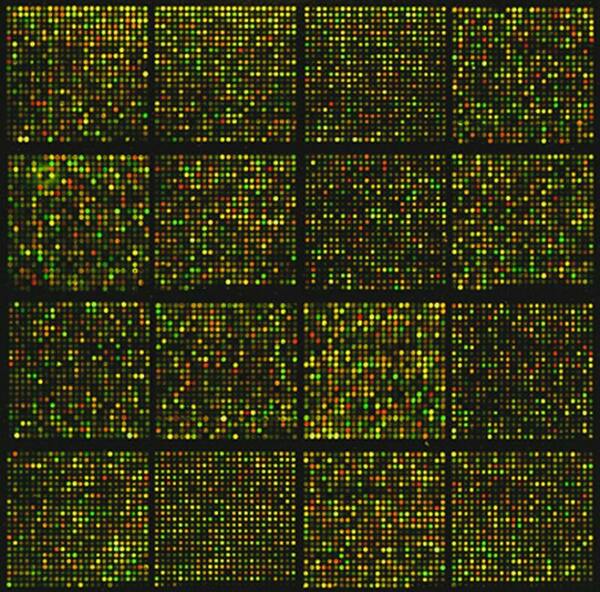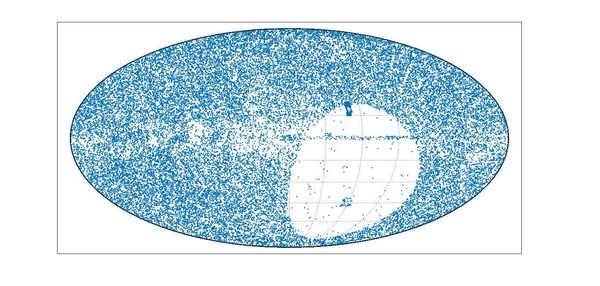
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is faint electromagnetic radiation left over from early stages in the formation of the universe. In order to analyze the CMB, scientists need to remove from electromagnetic data foreground radiation that contaminates CMB datasets. In this study, students utilize extensive updated datasets to analyze the correlation between CMB maps and Faraday RM and WMAP sky maps.
Read More...