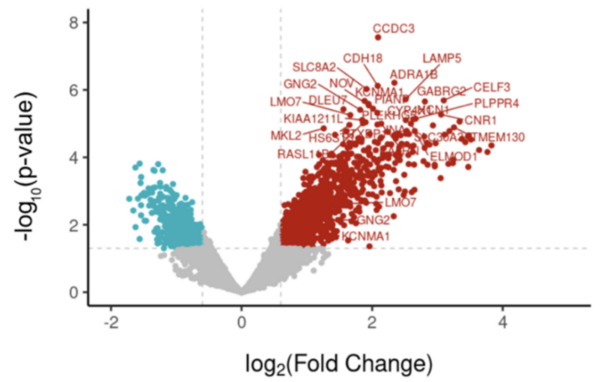
The authors looked at genes that were differentially expressed in patients who had and had not had febrile seizures to determine what differences in gene expression existed.
Read More...Gene expression analysis of febrile seizure’s impact on mesial temporal lobe epilepsy

The authors looked at genes that were differentially expressed in patients who had and had not had febrile seizures to determine what differences in gene expression existed.
Read More...A comparative study of food labels in the United States and India: Adherence to Codex Alimentarius guidelines
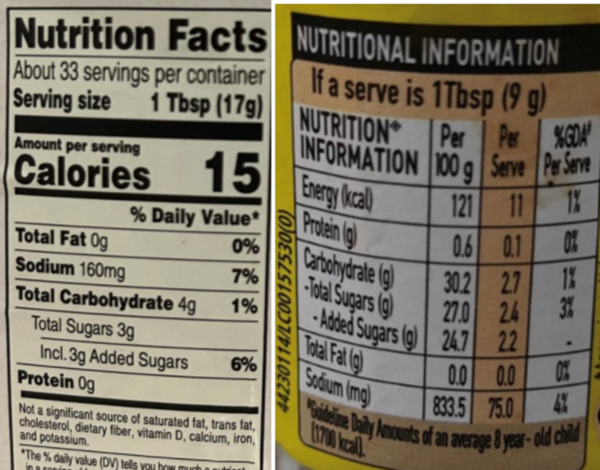
This study investigated how well food labels from 280 different brands across multiple food and drink categories in India and the US adhered to recommended nutritional labeling standards as outlined by the Codex Alimentarius.
Read More...Training neural networks on text data to model human emotional understanding

The authors train a neural network to detect text-based emotions including joy, sadness, anger, fear, love, and surprise.
Read More...Monitoring drought using explainable statistical machine learning models
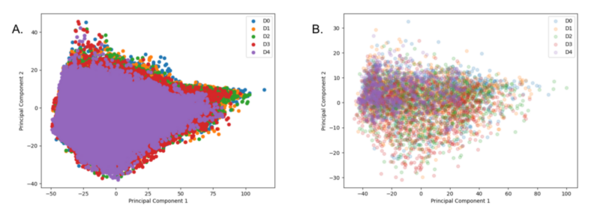
Droughts have a wide range of effects, from ecosystems failing and crops dying, to increased illness and decreased water quality. Drought prediction is important because it can help communities, businesses, and governments plan and prepare for these detrimental effects. This study predicts drought conditions by using predictable weather patterns in machine learning models.
Read More...Digestion products of bread and cheese cause addictive behavior in a planaria model
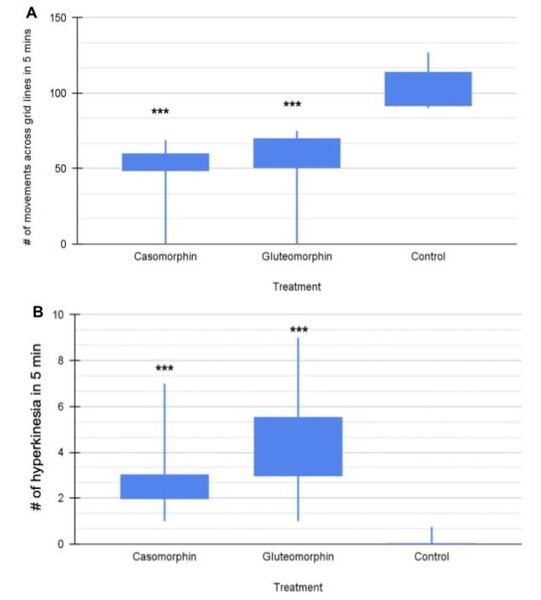
The authors looked at two peptides, gluteomorphin and casomorphin, that are present after the digestion of bread and cheese. As these peptides can bind opioid receptors the authors want to know if they could be addictive in the same way as conventional opioids (i.e., morphine) are known to be. Their results in a planaria model suggest that both of these peptides are addictive.
Read More...Ocean, atmosphere, and cloud quantity on the surface conditions of tidally-locked habitable zone planets
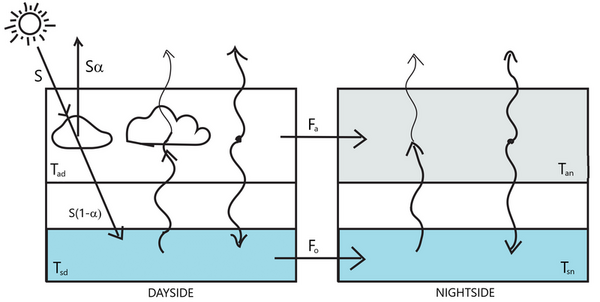
The authors assessed the atmospheric and oceanic parameters necessary for tidally-locked exoplanets to be habitable.
Read More...Investigating the inhibition of catabolic enzymes for implications in cardiovascular diseases and diabetes
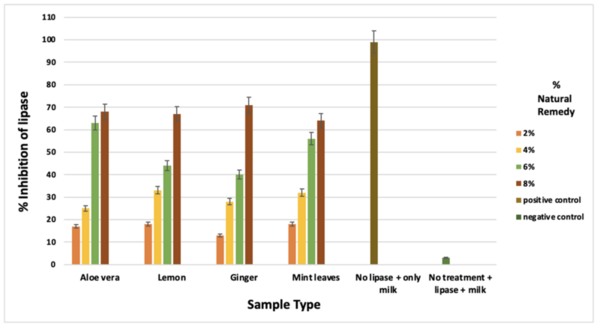
Enzymes that metabolize carbohydrates and lipids play a key role in our health, including global health challenges like cardiovascular diseases and diabetes. To learn more about these important enzymes, Gandhi and Gandhi test whether various natural substances (ginger, Aloe vera, lemon, and mint leaves) affect the activity of α-amylase and lipase enzymes.
Read More...Contribution of environmental factors to genetic variation in the Pacific white-sided dolphin

Here the authors sought to understand the effects of different variables that may be tied to pollution and climate change on genetic variation of Pacific white-sided dolphins, a species that is currently threatened by water pollution. Based on environmental data collected alongside a genetic distance matrix, they found that ocean currents had the most significant impact on the genetic diversity of Pacific white-sided dolphins along the Japanese coast.
Read More...Artificial intelligence assisted violin performance learning

In this study the authors looked at the ability of artificial intelligence to detect tempo, rhythm, and intonation of a piece played on violin. Technology such as this would allow for students to practice and get feedback without the need of a teacher.
Read More...Osmotic characteristics of water retention structures of Bursera microphylla in relation to soil salinity

This study hypothesized that sodium chloride was taken up through plant root structures to facilitate water transportation, and that sodium chloride accumulation was directly proportional to the soil salinity. Results showed that most cells within the “bulb” structures were isotonic at a concentration approximately twice as high as that of root tissue and ambient soil salinity, therefore supporting the presented hypothesis.
Read More...