Investigating the inhibition of catabolic enzymes for implications in cardiovascular diseases and diabetes
(1) Department of Science and Engineering, Barrington High School, (2) Department of Cardiology, Advocate Health Care
https://doi.org/10.59720/23-281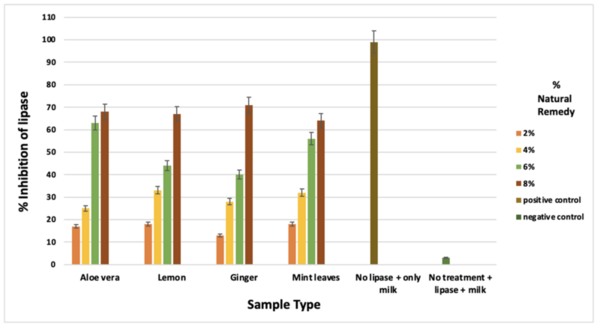
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are chronic health conditions characterized by their prolonged duration and non-infectious nature. These diseases, such as cardiovascular disease (CVD) and diabetes, are often influenced by a complex interplay of genetic, dietary, and lifestyle factors. Obesity, a major risk factor for both diabetes and CVDs, has been linked to excess consumption of carbohydrates and lipids. The enzymes α-amylase and lipase play key roles in the digestion and metabolism of carbohydrates and lipids, respectively. We hypothesized that four different natural substances, ginger, Aloe vera, lemon, and mint leaves, could inhibit the activity of α-amylase and lipase as a potential strategy to mitigate the risk of developing NCDs associated with obesity, CVD, and diabetes. Experimental model as follows: four natural substances were prepared at different concentrations. Solutions containing the enzymes amylase and lipase mixed with their respective buffers, were also made. The polyphenol solutions were then tested for their ability to inhibit the activity of α-amylase and lipase enzymes on their respective substances. Absorbance measurements were taken, and the percentage of enzyme inhibition was calculated for each natural remedy solution at varying concentrations. Experimental data showed that Aloe vera was more effective at inhibiting α-amylase, while ginger had the greatest inhibitory effect on lipase. Data also suggested a higher concentration of these natural substances had a higher inhibitory effect on both α-amylase and lipase enzymes. This study provides insights into natural alternatives that could potentially aid in the management and prevention of NCDs by targeting key enzymes involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates and lipids.
This article has been tagged with: