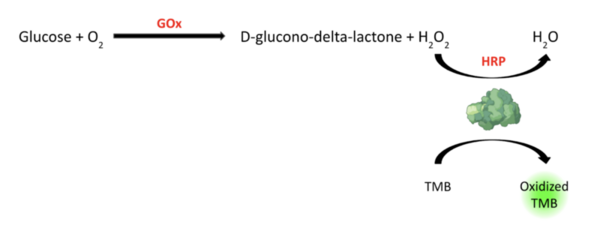
Here, recognizing that the immune response to cancer results in biomarkers that can be used to assess the immune status of cancer patients, the authors investigated the concentrations of key cytokines (TH1 and TH2 cytokines) in healthy controls and cancer patients. They identified significant changes in resting and activated cytokine profiles, suggesting that data of biomarkers such as these could serve as a starting point for further treatment with regard to a patient's specific immune profile.
Read More...

.jpg)