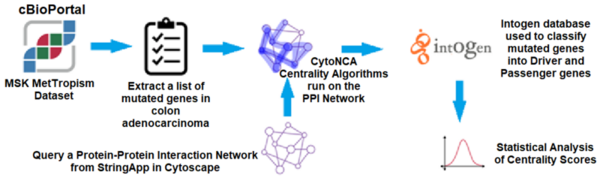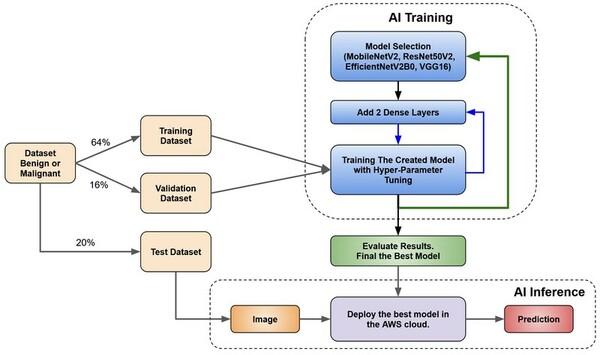
Skin cancer is a common and potentially deadly form of cancer. This study’s purpose was to develop an automated approach for early detection for skin cancer. We hypothesized that convolutional neural network-based models using transfer learning could accurately differentiate between benign and malignant moles using natural images of human skin.
Read More...