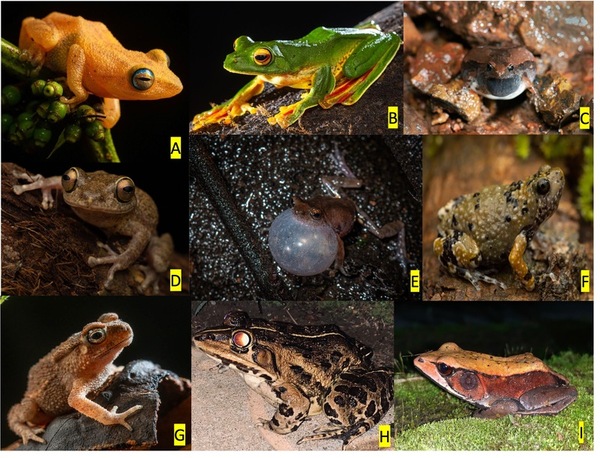
The mountain chain of the Western Ghats on the Indian peninsula, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is home to about 200 frog species, 89 of which are endemic. Distinctive to each frog species, their vocalizations can be used for species recognition. Manually surveying frogs at night during the rain in elephant and big cat forests is difficult, so being able to autonomously record ambient soundscapes and identify species is essential. An effective machine learning (ML) species classifier requires substantial training data from this area. The goal of this study was to assess data augmentation techniques on a dataset of frog vocalizations from this region, which has a minimal number of audio recordings per species. Consequently, enhancing an ML model’s performance with limited data is necessary. We analyzed the effects of four data augmentation techniques (Time Shifting, Noise Injection, Spectral Augmentation, and Test-Time Augmentation) individually and their combined effect on the frog vocalization data and the public environmental sounds dataset (ESC-50). The effect of combined data augmentation techniques improved the model's relative accuracy as the size of the dataset decreased. The combination of all four techniques improved the ML model’s classification accuracy on the frog calls dataset by 94%. This study established a data augmentation approach to maximize the classification accuracy with sparse data of frog call recordings, thereby creating a possibility to build a real-world automated field frog species identifier system. Such a system can significantly help in the conservation of frog species in this vital biodiversity hotspot.
Read More...