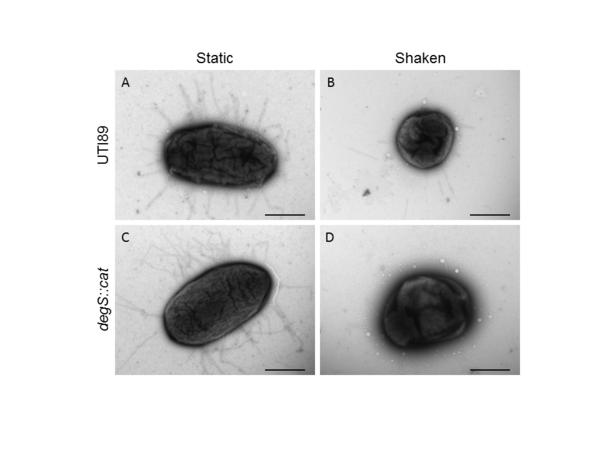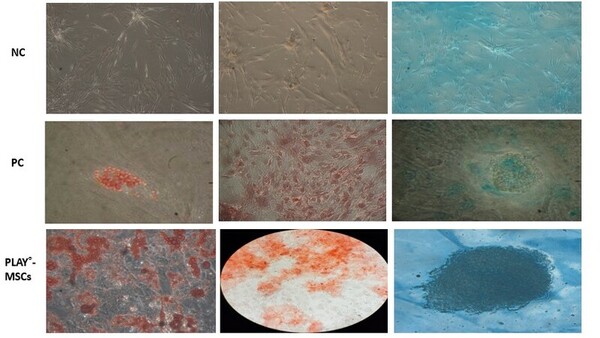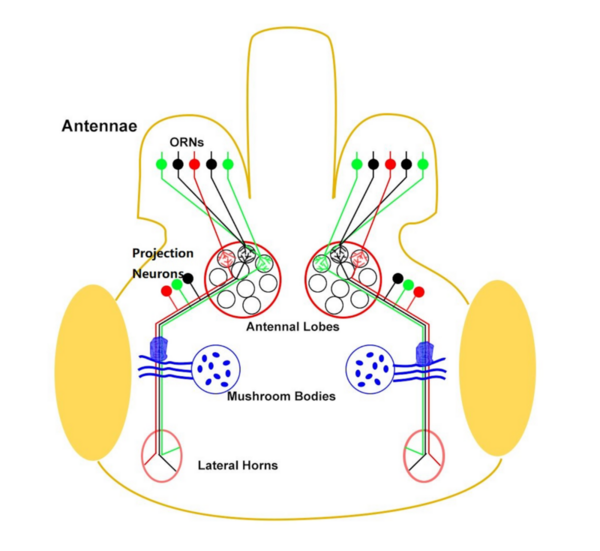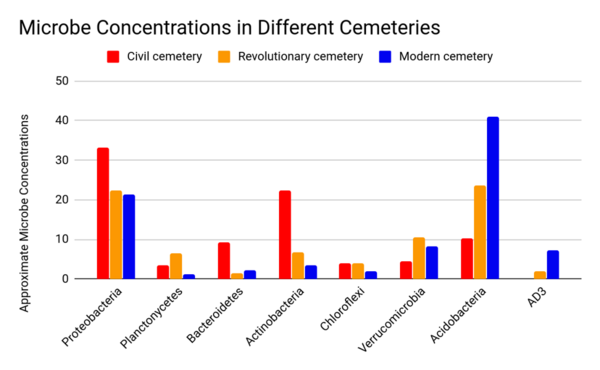
Previously established data indicate that cemeteries have contributed to groundwater and soil pollution, as embalming fluids can impact the microbiomes that exist in decomposing remains. In this study, Caputo et al hypothesized that microbial variation would be high between cemeteries from different eras due to dissimilarities between embalming techniques employed, and furthermore, that specific microbes would act as an indication for certain contaminants. Overall, they found that there is a variation in the microbiomes of the different eras’ cemeteries according to the concentrations of the phyla and their more specific taxa.
Read More...