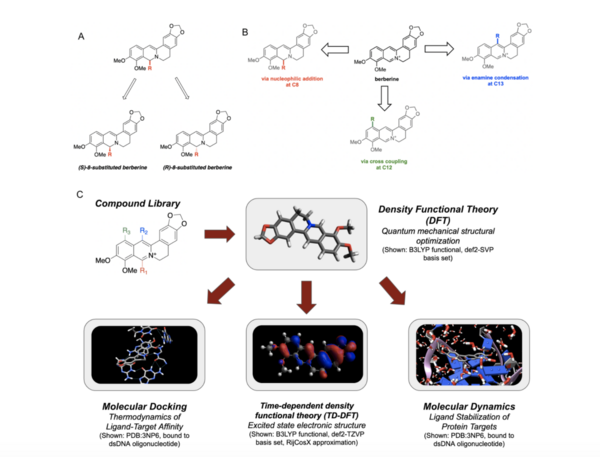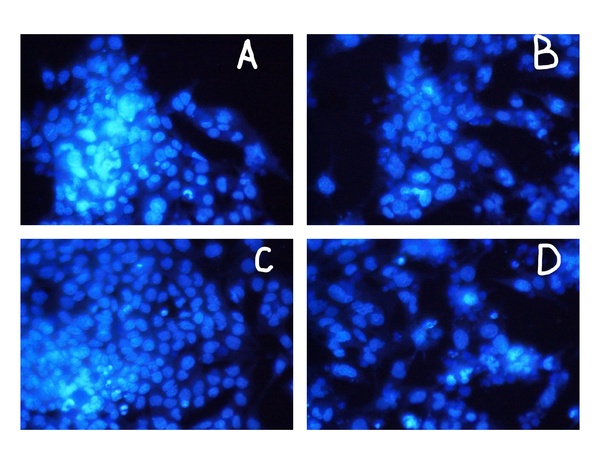
The purpose of our study was to determine if direct administration of CXCL1/KC to cardiomyocytes causes negative changes to cell density or proliferation. This molecule has been shown to reduce inflammation in certain instances. Homocysteine models the direct effect of an inflammatory agent on cardiomyocytes. Our question was whether these molecules directly impact cell density through an interaction with the cell proliferation process. We hypothesized that cells treated with CXCL1/KC would maintain the same cell density as untreated cells. In contrast, cells treated with Homocysteine or both Homocysteine and CXCL1/KC, were expected to have a higher cell density that than that of untreated cells.
Read More...


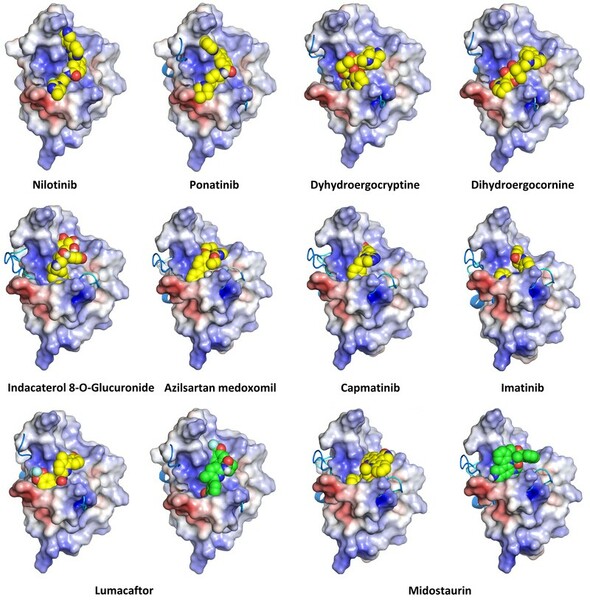

%20(1).png)