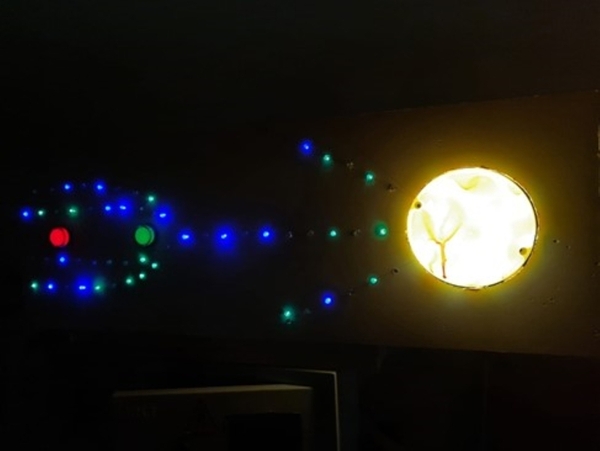

The authors propose and test a method that would allow for the generation of a magnetic field on Mars sufficient to support future colonization.
Read More...Generation of a magnetic field on Mars

The authors propose and test a method that would allow for the generation of a magnetic field on Mars sufficient to support future colonization.
Read More...Simulation of cosmic rays in the presence of a magnetic field
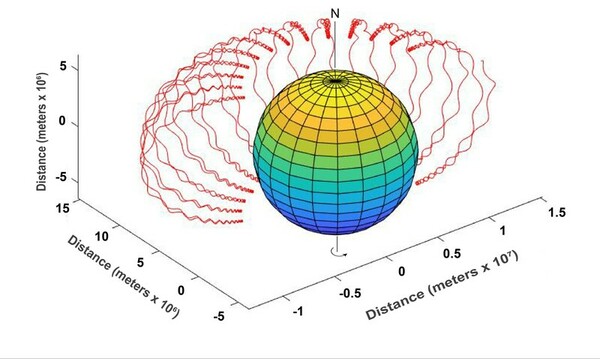
In this study the authors looked the trajectories of cosmic rays moving through a dipole field. They found that the trajectories of cosmic rays are determined by a particle's energy and interaction with Earth's B field.
Read More...Low environmental pH inhibits phagosome formation and motility of Tetrahymena pyriformis
.jpg)
In this study, the authors look into some of the implications of rising carbon dioxide levels by studying the effects of acidic pH on the ability of T. pyriformis to feed by quantifying phagosome formation and motility.
Read More...Phytoplankton Plastid Proteomics: Cracking Open Diatoms to Understand Plastid Biochemistry Under Iron Limitation
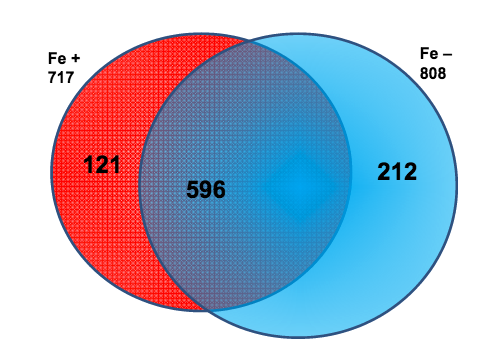
In many areas of the world’s oceans, diatoms such as Thalassiosira pseudonana are limited in growth by the availability of iron (Fe), which is an essential nutrient for diatoms. The authors of this study examined if Fe-limitation makes a significant difference in the proteins expressed within the chloroplast, the power source for diatoms, utilizing a new plastid isolation technique specific to diatoms and completing 14 mass spectrometry experiments.
Read More...Determining the Effect of Chemical and Physical Pretreatments on the Yield and Energy Output of Cellulosic Ethanol from Panicum Virgatum
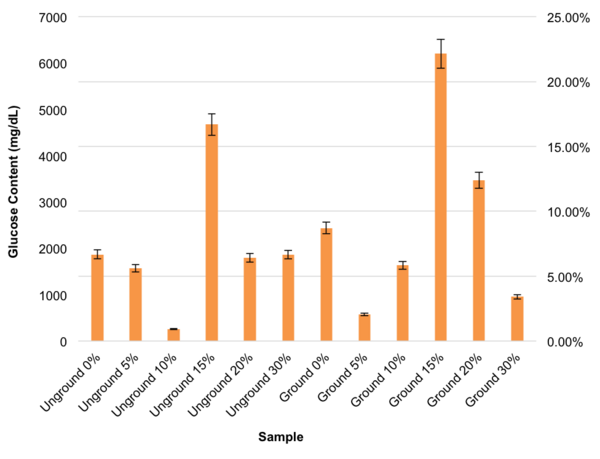
Fossil fuels are a limited resource; thus, it is important to explore new sources of energy. The authors examine the ability of switchgrass to produce ethanol and test the effects of pretreatment and grinding on ethanol yield.
Read More...An alternative to textile dyes: Synthesizing and applying PMMA nanoparticles to create structural coloration

The authors looked at developing a PMMA nanoparticle fabric dye that would be more sustainable compared to traditional fabric dyes. They were able to create PMMA based dyes in different colors that were also durable (i.e., did not fade quickly on fabric).
Read More...Examining the Growth of Methanotrophic Bacteria Immersed in Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields
Scientist are investigating the use of methane-consuming bacteria to aid the growing problem of rising greenhouse gas emissions. While previous studies claim that low-frequency electromagnetic fields can accelerate the growth rate of these bacteria, Chu et al. demonstrate that this fundamental ideology is not on the same wavelength with their data.
Read More...Influence of socioeconomic status on academic performance in virtual classroom settings

In this study, the authors conduct a survey to evaluate the impact of household socioeconomic status on effectiveness of distance learning for students.
Read More...Temperatures of 20°C Produce Increased Net Primary Production in Chlorella sp.
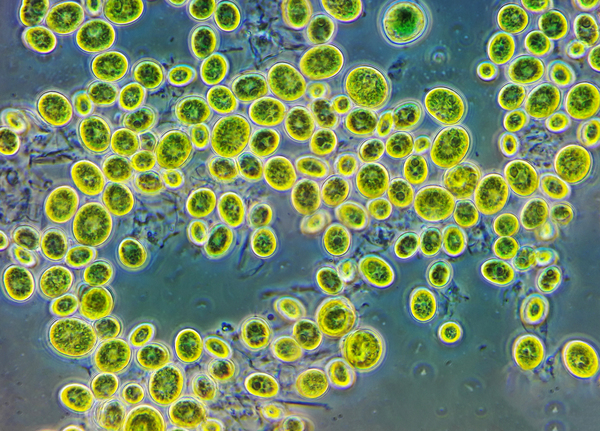
Chlorella sp. are unicellular green algae that use photosynthesis to reduce carbon dioxide into glucose. In this study, authors sought to determine the temperature that Chlorella sp. is maximally efficient at photosynthesis, and therefore removing the most carbon dioxide from the system. This activity could be harnessed to naturally remove carbon dioxide from the environment, fighting the effects of climate change.
Read More...Determining the Habitable Zone Around a Star
Life requires many things, including a hospitable temperature, elements, and energy. Here the authors utilize Newton's laws of physics and information relating a star's luminosity and temperature to determine the minimum and maximum masses and luminosities of planets and stars that would support life as we know it. This work can be used to determine the likelihood of a planet being able to support life based on attributes we can measure from here on Earth.
Read More...