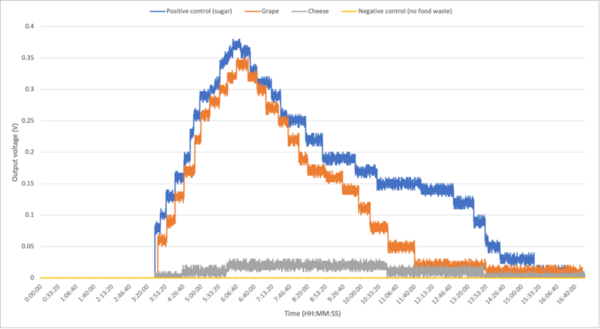
The authors look at how different food types impact the ability of bacteria to produce electricity.
Read More...The effects of food type on mediator-less microbial fuel cell electricity output

The authors look at how different food types impact the ability of bacteria to produce electricity.
Read More...Evaluating the clinical applicability of neural networks for meningioma tumor segmentation on 3D MRI
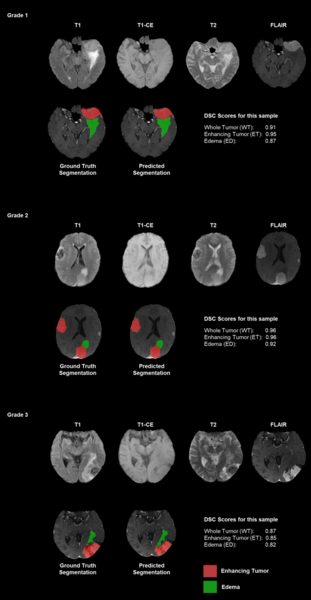
Authors emphasize the challenges of manual tumor segmentation and the potential of deep learning models to enhance accuracy by automatically analyzing MRI scans.
Read More...Breaking the Ice: A Scientific Take on the Ice Melting Abilities of Household Salts
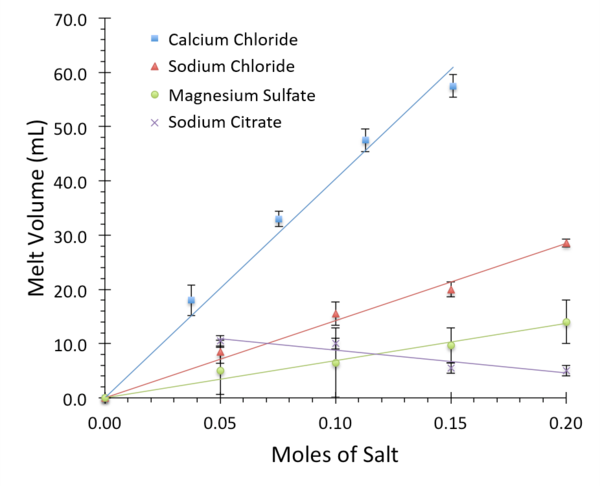
The use of salt to melt ice is a common and important practice to keep roadways safe during winter months. However, various subtypes of salt differ in their chemical and physical properties, as well as their environmental impact. In this study, the authors measure the effectiveness of different salts at disrupting ice structures and identify calcium chloride as the most effective.
Read More...Impact of gadodiamide (Omniscan) on a beef liver catalase ex vivo model
Here, seeking to better understand the effects of gadolinium-based contrast agents, dyes typically used for MRI scans, the authors evaluated the activity of catalase found in beef liver both with and without gadodiamide when exposed to hydrogen peroxide. They found that gadioamide did not significantly inhibit catalase's activity, attributing this lack of effects to the chelating agent found in gadodiamide.
Read More...Examining the Accuracy of DNA Parentage Tests Using Computer Simulations and Known Pedigrees

How accurate are DNA parentage tests? In this study, the authors hypothesized that current parentage tests are reliable if the analysis involves only one or a few families of yellow perch fish Perca flavescens. Their results suggest that DNA parentage tests are reliable as long as the right methods are used, since these tests involve only one family in most cases, and that the results from parentage analyses of large populations can only be used as a reference.
Read More...Examining What Causes Perceived Dissonance in Musical Intervals and the Effect of Timbre on Dissonance

Music is an important part of the day for many of us, but what makes some combinations of sound more pleasant to the ear than others? In this article the authors investigate the role of some characteristics of sound on the perception of a pleasant vs harsh musical note.
Read More...Modelling effects of alkylamines on sea salt aerosols using the Extended Aerosols and Inorganics Model

With monitoring of climate change and the evolving properties of the atmosphere more critical than ever, the authors of this study take sea salt aerosols into consideration. These sea salt aerosols, sourced from the bubbles found at the surface of the sea, serve as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) and are effective for the formation of clouds, light scattering in the atmosphere, and cooling of the climate. With amines being involved in the process of CCN formation, the authors explore the effects of alkylamines on the properties of sea salt aerosols and their potential relevance to climate change.
Read More...Variations in Heat Absorption and Release of Earth Surfaces During Fall in Laramie, Wyoming
Here the authors investigate the contributions of man-made surfaces in Laramie, Wyoming to the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect. Heat absorption and release by five surfaces were measured in the autumn of 2018. By recording temperatures of man-made and natural surfaces at early morning, mid-afternoon, and evening using an infrared thermometer, the authors determined that man-made surfaces retained more heat in fall than natural surfaces.
Read More...Identification of potential therapeutic targets for multiple myeloma by gene expression analysis
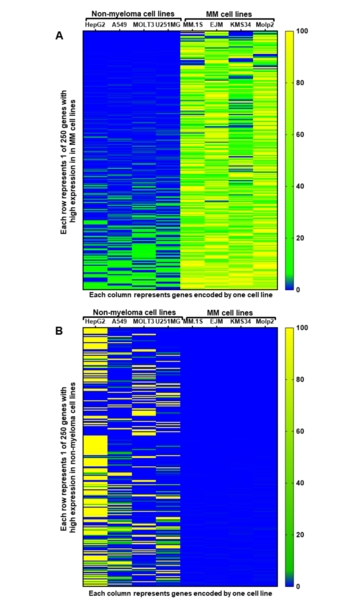
A central challenge of cancer therapy is identifying treatments that will effectively target cancer cells while minimizing effects on healthy cells. To identify potential targets for treating a multiple myeloma, a frequently incurable cancer, Kochenderfer and Kochenderfer analyze RNA sequencing data from the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia to find genes with high expression in multiple myeloma cells and low expression in normal tissues
Read More...The Effects of L-glutamate, L-glutamine, and L-aspartic Acid on the Amylase Production of E. coli Transformed With pAmylase
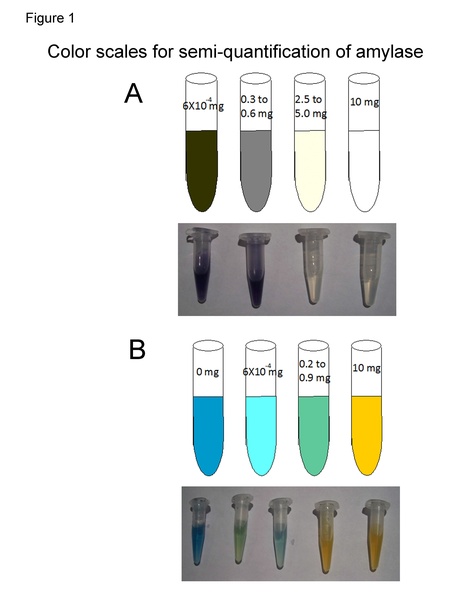
Human amylase is important to digestion and has broad applications for therapeutic use in patients with pancreatic insufficiency. The authors present a method to increase amylase production in E. coli by adding the amino acids L-glutamate and L-glutamine.
Read More...Search articles by title, author name, or tags