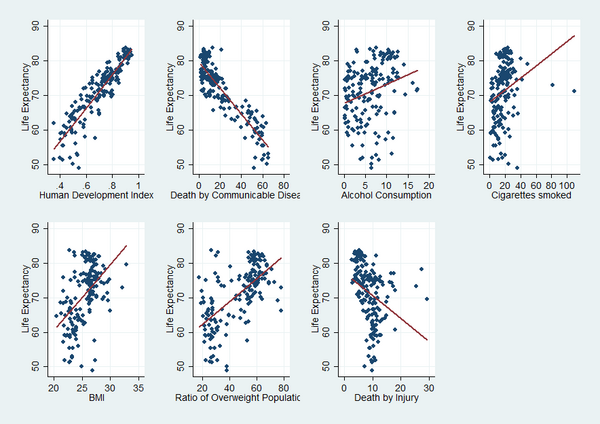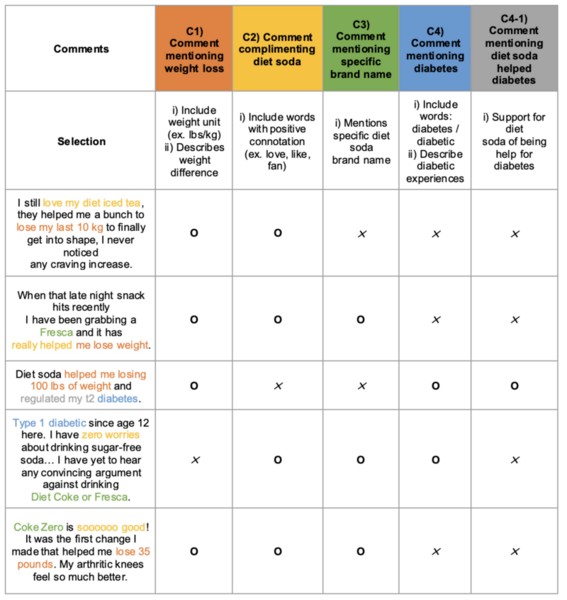
Artificial sweeteners are rising in popularity, in part due to the influence of social media platforms like YouTube. However, YouTube commenters often repeat information about artificial sweeteners that is not supported by scientific research. To investigate how misinformation about sweeteners spreads through social media, Kim and Yoo conduct a content analysis of YouTube comments to reveal how many comments repeat misinformation about artificial sweeteners' effects.
Read More...

.png)