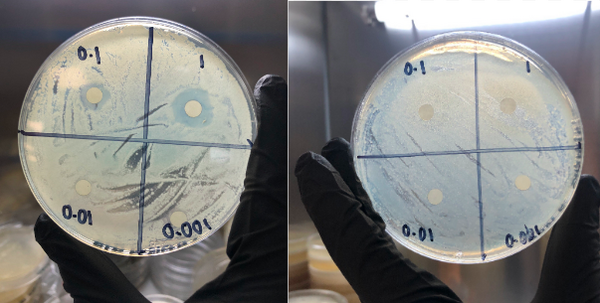
In this study, the authors investigated the antimicrobial properties of the tree species, Populus balsamifera. It was observed that the extract of the buds of P. balsamifera was highly effective against gram-positive bacteria. This helps to indicate the potential use of P. balsamifera in the medical field to eliminate gram-positive bacteria.
Read More...