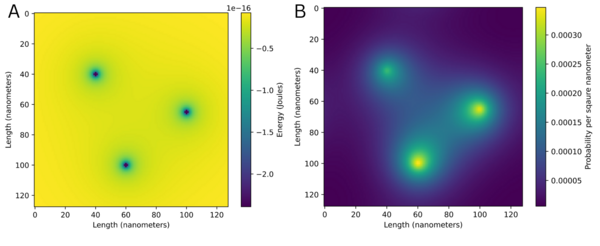
The authors use the Lanczos algorithm to computationally solve the Schrodinger equation for 2D potentials with a Python program
Read More...Solving the Schrödinger equation computationally using the Lanczos algorithm

The authors use the Lanczos algorithm to computationally solve the Schrodinger equation for 2D potentials with a Python program
Read More...Photometric analysis and light curve modeling of apparent transient 2020pni

Supernovas are powerful explosions that result from gravitational collapse of a massive star. Using photometric analysis Arora et al. set out to investigate whether 2020pni (located in galaxy UGC 9684) was a supernova. They were ultimately able to identify 2020pni as a Type II-L supernova and determine it's distance from earth.
Read More...Comparing Measurements of Sun-Earth Distance: Shadow Method and Two Pinhole Method Variations
This study compares three methods regarding their accuracy in calculating the distance between the Earth and the Sun. The hypothesis presented was that the shadow method would have the greatest mean accuracy, followed by the tube pinhole method, and finally the plate pinhole method. The results validate the hypothesis; however, further investigation would be helpful in determining effective mitigation of each method’s limitations and the effectiveness of each method in determining the distance of other light-emitting objects distant from the Earth.
Read More...A study on the stretching behavior of rubber bands

Here, the authors considered the stretching behavior of rubber bands by exposing the rubber bands to increasing loads and measuring their stretch response. They found that a linear stretch response was observed for intermediate loading steps, but this behavior was lost at lower or higher loads, deviating from Hooke's Law. The authors suggest that studies such as these can be used to evaluate other visco-elastic structures.
Read More...Determining surface tension of various liquids and shear modulus of paper using crumpling effect
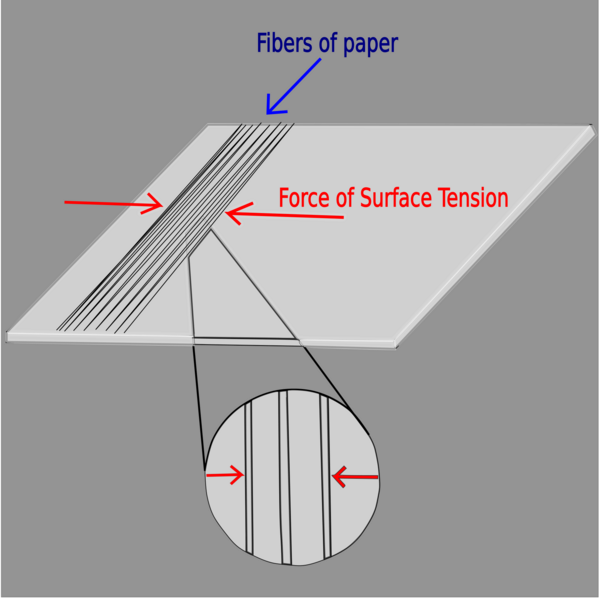
In this article, the authors investigate the shear modulus of different types of paper in the setting of the crumpling effect.
Read More...The Effects of Atmospheric Attenuation on Cosmic Ray Muons: How is Surface Level Cosmic Ray Muon Flux Affected by Atmospheric Attenuation?
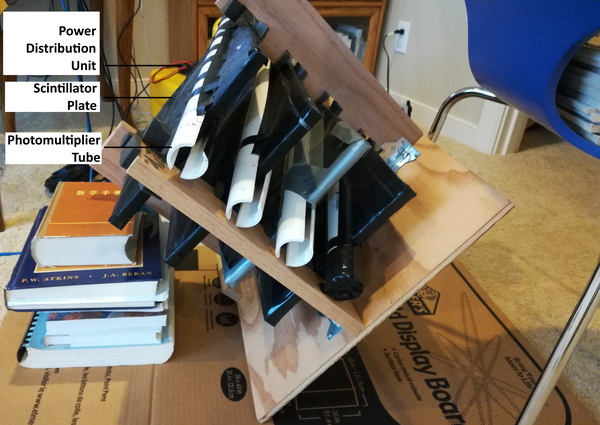

Cosmic rays are high-energy astronomical particles originating from various sources across the universe. Here, The authors sought to understand how surface-level cosmic-ray muon flux is affected by atmospheric attenuation by measuring the variation in relative muon-flux rate relative to zenith angle, testing the hypothesis that muons follow an exponential attenuation model. The attenuation model predicts an attenuation length of 6.3 km. This result implies that only a maximum of 24% of muons can reach the Earth’s surface, due to both decay and atmospheric interactions.
Read More...Optimizing 3D printing parameters: Evaluating infill type and layer height effects on tensile fracture force
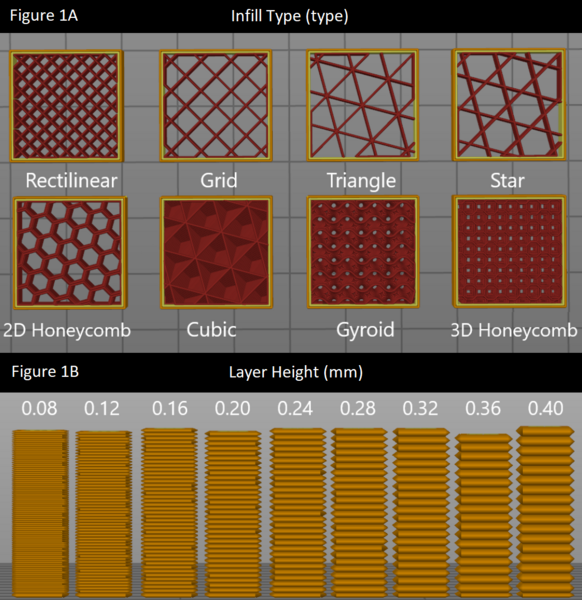
In this study, the authors test different infill patterns to determine which would be the strongest and most durable for 3D printing applications, which have become an integral part of many facets of life.
Read More...Predicting Orbital Resonance of 2867 Šteins Using the Yarkovsky Effect
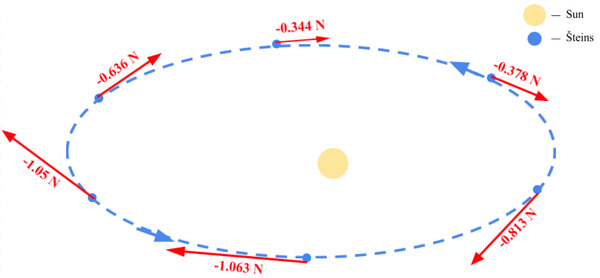
In this study, the impact of thermal effects on the orbit of an asteroid is investigated. This included determining if the asteroid's orbit would push into a region devoid of asteroids due to the gravitational pull of Jupiter.
Read More...Alterations of the [Fe/H] Values Modulate Light Curves by Absolute Magnitude in non-Blazhko RRab Lyraes
![Alterations of the [Fe/H] Values Modulate Light Curves by Absolute Magnitude in non-Blazhko RRab Lyraes](/rails/active_storage/representations/proxy/eyJfcmFpbHMiOnsibWVzc2FnZSI6IkJBaHBBallHIiwiZXhwIjpudWxsLCJwdXIiOiJibG9iX2lkIn19--7d8b84074a7b504657e6acd5ed4f66e4b84daf63/eyJfcmFpbHMiOnsibWVzc2FnZSI6IkJBaDdCem9MWm05eWJXRjBTU0lJY0c1bkJqb0dSVlE2QzNKbGMybDZaVWtpRFRZd01IZzJNREErQmpzR1ZBPT0iLCJleHAiOm51bGwsInB1ciI6InZhcmlhdGlvbiJ9fQ==--33b2b080106a274a4ca568f8742d366d42f20c14/Figure_4.png)
In this study, the authors investigate the relationship between iron/hydrogen ratio [Fe/H] of a type of variable stars commonly used as reference points RR Lyrae stars and their light curves to see if one can determine the composition of these stars solely by measuring their light curve characteristics.
Read More...Analysis of the effects of positive ions and boundary layer temperature at various hypersonic speeds on boundary layer density
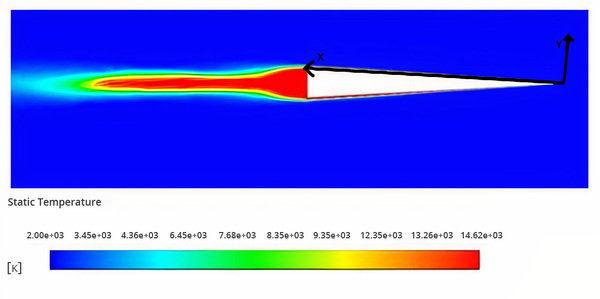
This study's goal was to identify the Mach numbers for which electrostatic drag and heat transfer manipulation would be most applicable inside the stratosphere. The experiments were conducted using computational fluid dynamics software. The study demonstrated that, on average, higher Mach speeds resulted in a considerably higher potential decrease in density. The study highlights that further research on the surface charge method is warranted to explore higher hypersonic speeds within the stratosphere.
Read More...Search articles by title, author name, or tags