
The authors use machine learning on MRI images of brain tissue to predict tumor onset as an avenue for early detection of brain cancer.
Read More...A comparative analysis of machine learning approaches to predict brain tumors using MRI

The authors use machine learning on MRI images of brain tissue to predict tumor onset as an avenue for early detection of brain cancer.
Read More...Deuterated solvent effects in the kinetics and thermodynamics of keto-enol tautomerization of ETFAA
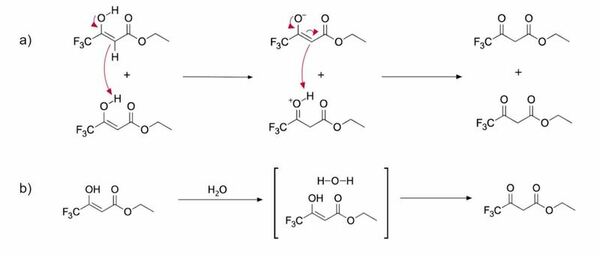
In this study, the authors determined whether tautomerization dynamics in protic and aprotic solvents displayed differences in reaction rates and in the proportion of the keto and enol tautomers present.
Read More...India’s digital public infrastructure: Analyzing UPI and Aadhaar in GDP growth and cost optimization
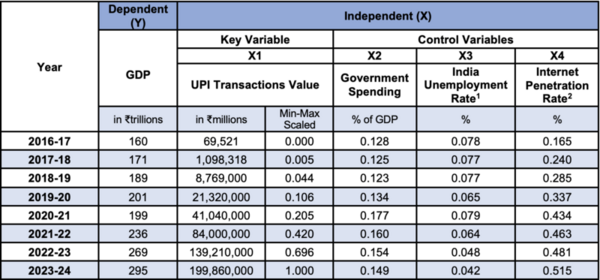
India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)—including the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and Aadhaar—has been globally recognized for advancing financial inclusion and efficient governance. This study analyzes data from 2016–17 to 2023–24 the impact of these services on India's GDP.
Read More...Deep dive into predicting insurance premiums using machine learning
The authors looked at different factors, such as age, pre-existing conditions, and geographic region, and their ability to predict what an individual's health insurance premium would be.
Read More...Using advanced machine learning and voice analysis features for Parkinson’s disease progression prediction
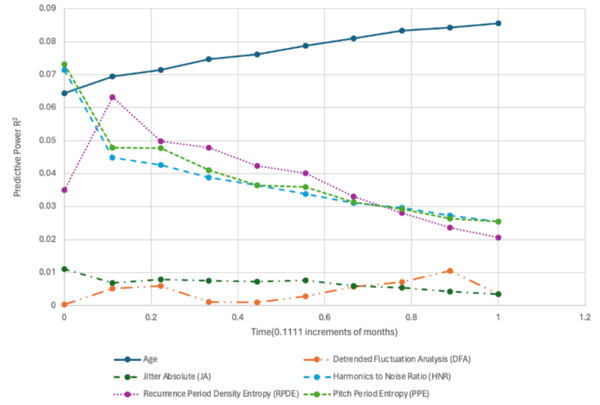
The authors looked at the ability to use audio clips to analyze the progression of Parkinson's disease.
Read More...Genetic algorithm based features selection for predicting the unemployment rate of India

The authors looked at using genetic algorithms to look at the Indian labor market and what features might best explain any variation seen. They found that features such as economic growth and household consumption, among others, best explained variation.
Read More...Using explainable artificial intelligence to identify patient-specific breast cancer subtypes
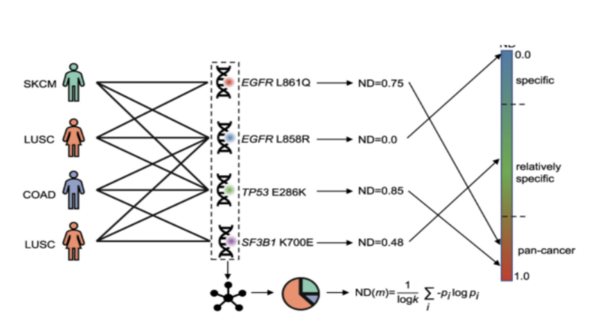
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women, with approximately 300,000 diagnosed with breast cancer in 2023. It ranks second in cancer-related deaths for women, after lung cancer with nearly 50,000 deaths. Scientists have identified important genetic mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 that lead to the development of breast cancer, but previous studies were limited as they focused on specific populations. To overcome limitations, diverse populations and powerful statistical methods like genome-wide association studies and whole-genome sequencing are needed. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) can be used in oncology and breast cancer research to overcome these limitations of specificity as it can analyze datasets of diagnosed patients by providing interpretable explanations for identified patterns and predictions. This project aims to achieve technological and medicinal goals by using advanced algorithms to identify breast cancer subtypes for faster diagnoses. Multiple methods were utilized to develop an efficient algorithm. We hypothesized that an XAI approach would be best as it can assign scores to genes, specifically with a 90% success rate. To test that, we ran multiple trials utilizing XAI methods through the identification of class-specific and patient-specific key genes. We found that the study demonstrated a pipeline that combines multiple XAI techniques to identify potential biomarker genes for breast cancer with a 95% success rate.
Read More...Determining the best convolutional neural network for identifying tuberculosis and pneumonia in chest x-rays
.png)
To best identify tuberculosis and pneumonia diagnoses in chest x-rays, the authors compare different deep learning convolution neural networks.
Read More...The Effects of Altered Microbiome on Caenorhabditis elegans Egg Laying Behavior
Since the discovery that thousands of different bacteria colonize our gut, many of which are important for human wellbeing, understanding the significance of balancing the different species on the human body has been intensely researched. Untangling the complexity of the gut microbiome and establishing the effect of the various strains on human health is a challenge in many circumstances, and the need for simpler systems to improve our basic understanding of microbe-host interactions seems necessary. C. elegans are a well-established laboratory animal that feed on bacteria and can thus serve as a less complex system for studying microbe-host interactions. Here the authors investigate how the choice of bacterial diet affects worm fertility. The same approach could be applied to many different outcomes, and facilitate our understanding of how the microbes colonizing our guts affect various bodily functions.
Read More...Computational evidence for differential endocrine disruption by DEHP and PET via estrogen receptor beta binding
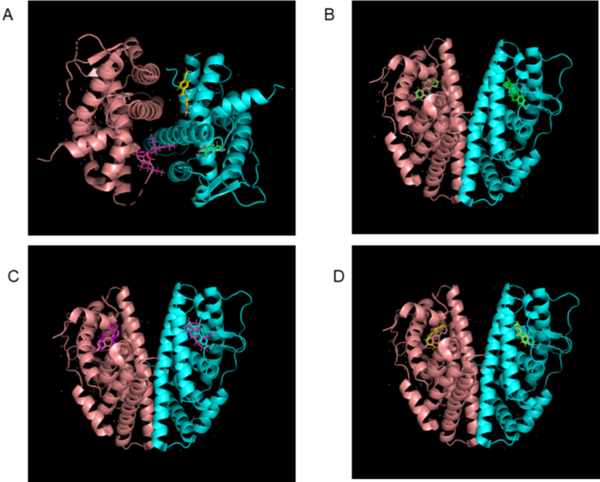
The authors demonstrate computationally that two types of nanoplastics can bind to estrogen receptor beta and potentially disrupt endocrine systems.
Read More...