.jpg)
In this study, the authors look into some of the implications of rising carbon dioxide levels by studying the effects of acidic pH on the ability of T. pyriformis to feed by quantifying phagosome formation and motility.
Read More...Low environmental pH inhibits phagosome formation and motility of Tetrahymena pyriformis
.jpg)
In this study, the authors look into some of the implications of rising carbon dioxide levels by studying the effects of acidic pH on the ability of T. pyriformis to feed by quantifying phagosome formation and motility.
Read More...A Statistical Comparison of the Simultaneous Attack/ Persistent Pursuit Theory Against Current Methods in Counterterrorism Using a Stochastic Model
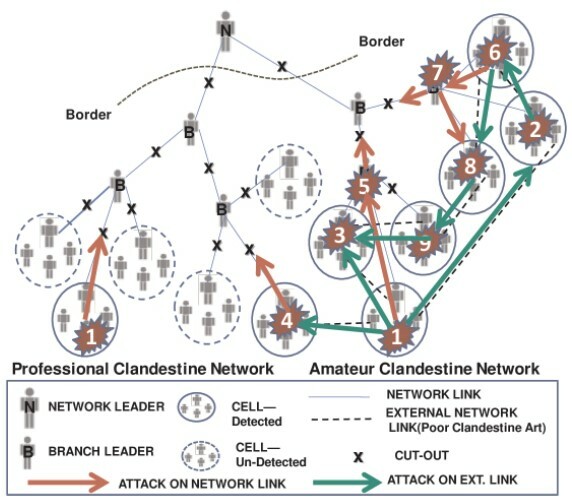
Though current strategies in counterterrorism are somewhat effective, the Simultaneous Attack/Persistent Pursuit (SAPP) Theory may be superior alternative to current methods. The authors simulated five attack strategies (1 SAPP and 4 non-SAPP), and concluded that the SAPP model was significantly more effective in reducing the final number of terrorist attacks. This demonstrates the comparative advantage of utilizing the SAPP model, which may prove to be critical in future efforts in counterterrorism.
Read More...POC-MON: A Novel and Cost-Effective Pocket Lemon Sniff Test (PLST) for Early Detection of Major Depressive Disorder
Effective treatment of depression requires early detection. Depressive symptoms overlap with olfactory regions, which led to several studies of the correlation between sense of smell and depression. The alarming rise of depression, its related crimes, suicides, and lack of inexpensive, quick tools in detecting early depression — this study aims in demonstrating decreased olfaction and depression correlation. Forty-two subjects (ages 13-83) underwent POC-MON (Pocket Lemon) assessment — an oven-dried lemon peel sniff test, subjected to distance measurement when odor first detected (threshold) and completed Patient Health Questionnaires (PHQ-9). POC-MON and PHQ-9 scores yielded a correlation of 20% and 18% for the right and left nostrils, respectively. Among male (n=17) subjects, the average distance of POC-MON and PHQ-9 scores produced a correlation of 14% and 16% for the right and left nostrils, respectively. Females (n=25) demonstrated a correlation of 28% and 21% for the right and left nostrils, respectively. These results suggest the correlation between olfaction and depression in diagnosing its early-stage, using a quick, inexpensive, and patient-friendly tool — POC-MON.
Read More...The Effect of Different Fructose Diets on the Lifespan of C. elegans
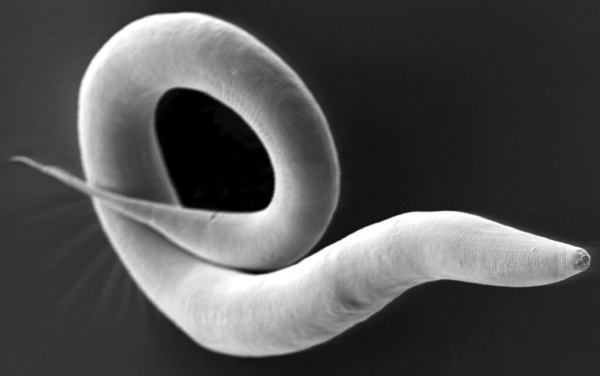
High-fructose diets consumed widely in modern societies predisposes to metabolic diseases such as diabetes. Using the worm C. elegans, the authors of this study investigated the effect of fructose on the worm's survival rates. They found that worms fed 15% fructose had a lower life expectancy than those on a fructose-free diet. These results suggest that, like in humans, fructose has a negative effect on worm survival, which makes them an easy, attractive model to study the effects of fructose on health.
Read More...Synergistic Effects of Metformin and Captopril on C. elegans
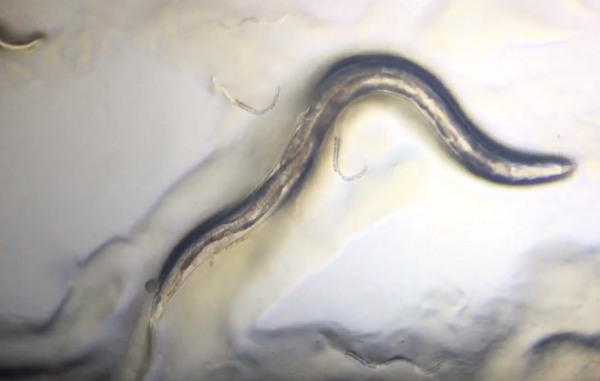
Kadıoğlu and Oğuzalp study the synergistic effects of Metformin and Captopril, two commonly prescribed drugs for type 2 diabetes and hypertension, respectively. Using C. elegans nematodes as a model system, the authors find that the nematodes decreased in average body length when exposed to Metformin or Captopril individually, but grew 11% in body length when both drugs were used together. Because C. elegans body size is regulated in part by the TGF-β signaling pathway, the authors suggest that synergistic effects of these two drugs may be modulating TGF-β activity, a previously uncharacterized phenomenon.
Read More...The effect of nicotine and lead on neuron morphology, function, and ɑ-Synuclein levels in a C. elegans model
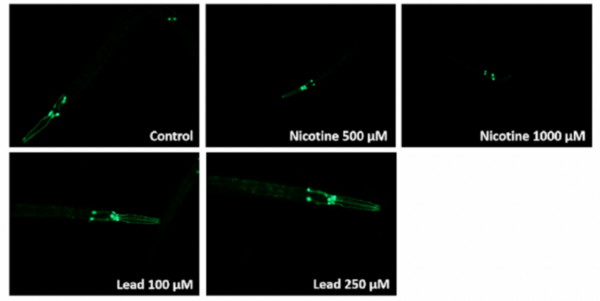
E-cigarettes are often considered a healthier alternative to traditional cigarettes. This team of high school authors investigated the impact of common e-cigarette compounds on C. elegans, and found a number of harmful effects ultimately resulting in injury and neuronal damage.
Read More...Using CRISPR technology to inhibit the replication of human cytomegalovirus by deletion of a gene promoter
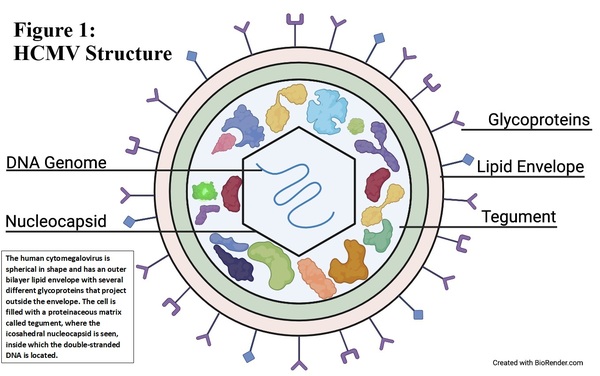
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) causes serious infections in immunocompromised patients and therapies to inhibit latent HCMV are not developed. Using CRISPR/Cas9, the authors were able to delete an important promoter region in HCMV.
Read More...Observing effects of resolving leaky gut on sugar, fat, and insulin levels during type 1 diabetes in fruit flies

This study uses a fruit fly model of type 1 diabetes (T1D) to determine whether strengthening intestinal tight junctions to reduce intestinal permeability would improve T1D symptoms.
Read More...Astragalus membranaceus Root Concentration and Exposure Time: Role in Heat Stress Diminution in C. elegans

In this study, the authors investigated the biological mechanism underlying the actions of a traditional medicinal plant, Astragalus membranaceus. Using C. elegans as an experimental model, they tested the effects of AM root on heat stress responses. Their results suggest that AM root extract may enhance the activity of endogenous pathways that mediate cellular responses to heat stress.
Read More...A novel bioreactor system to purify contaminated runoff water
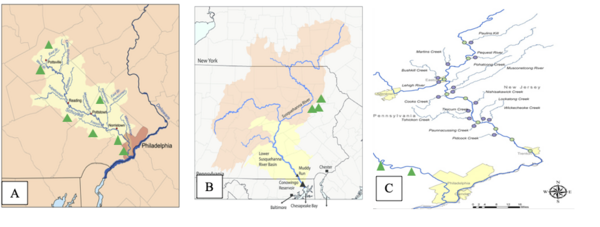
In this study, the authors engineer a cost-effective and bio-friendly water purification system using limestone, denitrifying bacteria, and sulfate-reducing bacteria. They evaluated its efficacy with samples from Eastern PA industrial sites.
Read More...Search articles by title, author name, or tags