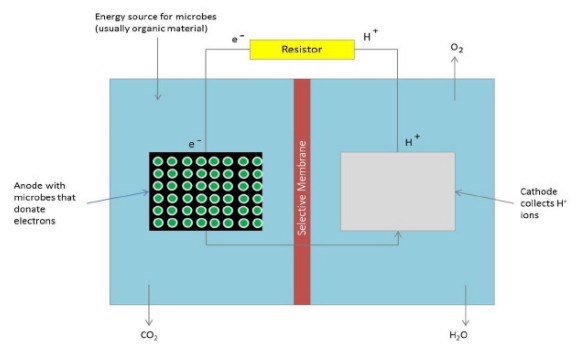
Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are bio-electrochemical systems that utilize bacteria and are promising forms of alternative energy. Similar to chemical fuel cells, MFCs employ both an anode (accepts electrons) and a cathode (donates electrons), but in these devices the live bacteria donate the electrons necessary for current. In this study, the authors assess the functionality of a photosynthetic MFC that utilizes a purple non-sulfur bacterium. The MFC prototype they constructed was found to function over a range of environmental conditions, suggesting its potential use in industrial models.
Read More...



.png)