The authors looked at how soil temperature changes with fire to develop a sensor system that could aid in earlier detection of fires.
Read More...Browse Articles
Growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Escherichia coli when exposed to anti-acne vitamin A
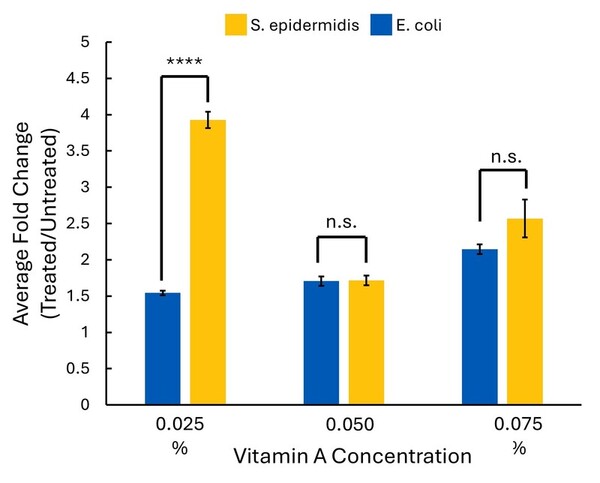
The authors looked at the impact of vitamin A (retinol) on growth of S. epidermidis (most abundant bacterium on the skin) and E. coli (found in the gut microbiome, but not on the skin).
Read More...Initiating astrocyte to neuron transdifferentiation via miR-124a: implications in neurodegenerative disease
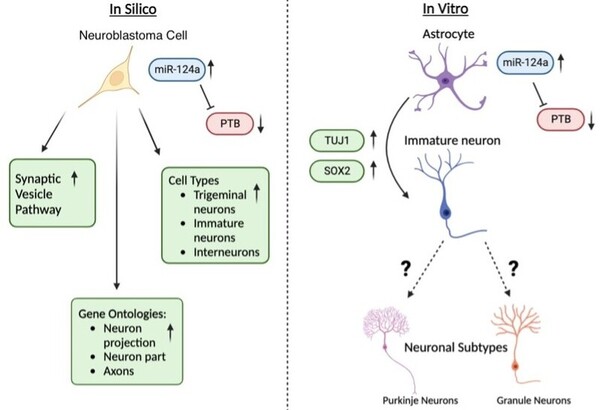
The authors looked at whether they could induce the formation of new neurons from astrocytes via the upregulation of a microRNA (miR-124a). They found that upregulation of miR-124a started transdifferentiation of neurons, but was not enough to lead to full conversion of astrocytes to neurons.
Read More...A 1D model of ultrasound waves for diagnosing of hepatomegaly and cirrhosis
The authors created a 1D model to diagnose hepatomegaly and cirrhosis via ultrasound of the liver.
Read More...Crystallization kinetics of vanillin thin films
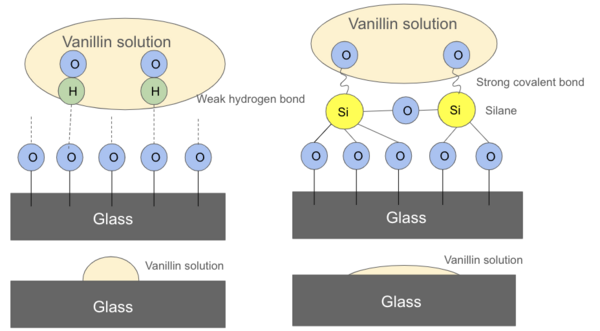
In this study, the authors investigate the crystallization kinetics of vanillin thin films from a solution or a melt, as well as how a silane coating on the glass surface affects these properties.
Read More...Depression detection in social media text: leveraging machine learning for effective screening
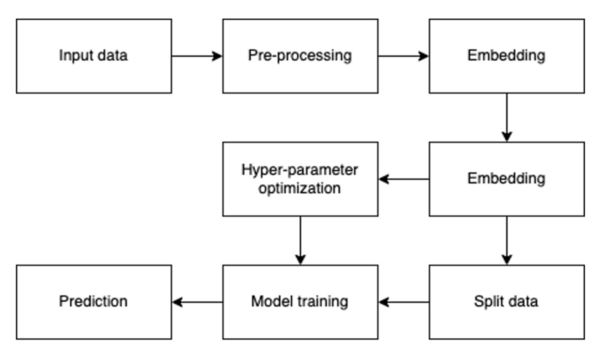
Depression affects millions globally, yet identifying symptoms remains challenging. This study explored detecting depression-related patterns in social media texts using natural language processing and machine learning algorithms, including decision trees and random forests. Our findings suggest that analyzing online text activity can serve as a viable method for screening mental disorders, potentially improving diagnosis accuracy by incorporating both physical and psychological indicators.
Read More...Impact of environmental stressors on ultrasonic acoustic emissions in different species of plants
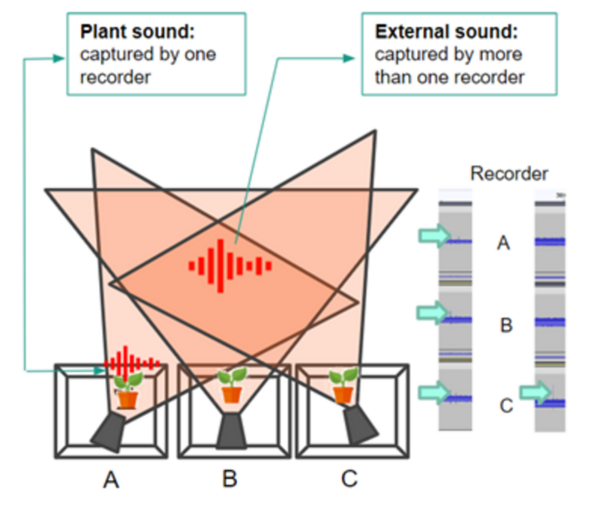
Current horticulture practices often rely on pesticides, causing environmental harm. To address this, authors explore the use of ultrasonic sound emissions to detect plant stress at an individual level.
Read More...The optimization of high-protein duckweed cultivation in eutrophicated water with mutualistic bacteria
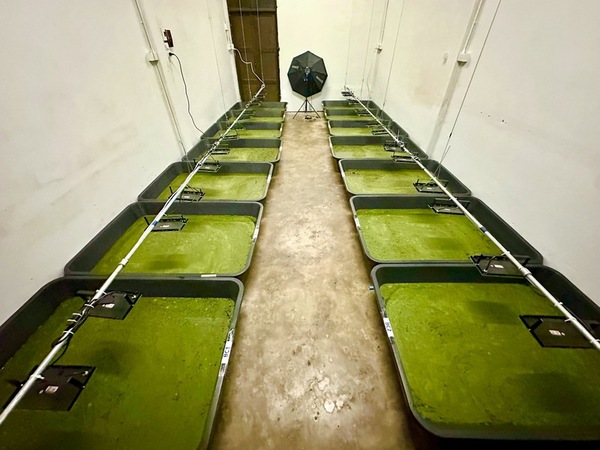

he rapid growth of the human population is driving food crises in Thailand and Southeast Asia, while contributing to global food insecurity and a larger carbon footprint. One potential solution is cultivating duckweed (Wolffia globosa) for consumption, as it grows quickly and can provide an alternative protein source. This research explored two methods to optimize duckweed cultivation: using phosphorus- and nitrogen-rich growing media and plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB).
Read More...School sustainability: The implications of implementing living walls at schools for air purification

The authors compare air quality in the presence and absence of a living wall in a high school hallway in Brooklyn, NY.
Read More... A low-cost method for purification of agricultural wastewater based on S. platensis
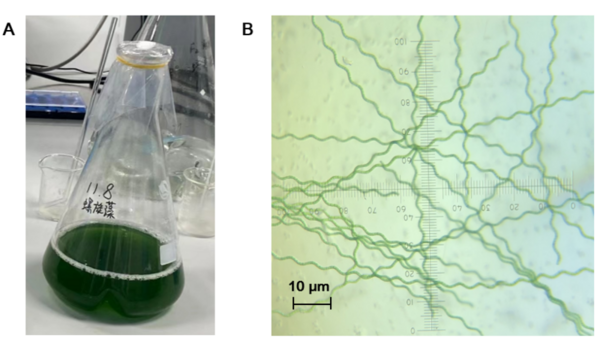
The authors looked at the ability of Spirulina platensis to reduce contaminants in wastewater in order to develop a more accessible treatment option. They found that S platensis did reduce the concentration of pollutants present within simulated agricultural wastewater.
Read More...