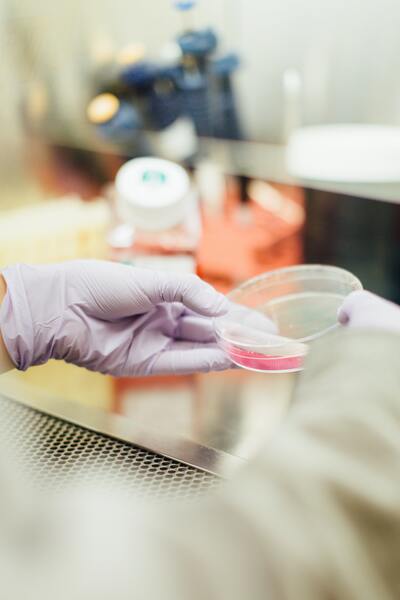
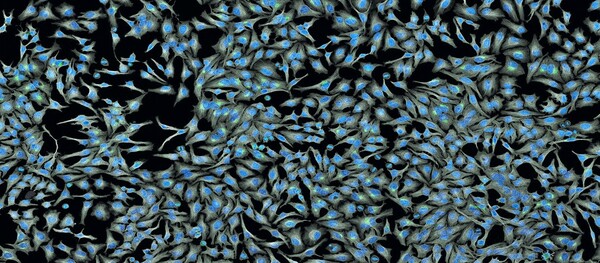
Regenerative medicine has become a mainstay in recent times, and employing stem cells to treat several degenerative, inflammatory conditions has resulted in very promising outcomes. These forms of cell-based therapies are novel approaches to existing treatment modalities. In this study, the authors compared the concentrations of the cytokines PDGF, IL-8, and VEGF between conditioned and spent media of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to evaluate their potential therapeutic properties for wound healing in inflammatory conditions. They hypothesized that conditioned media contains higher concentrations of wound healing cytokines compared to spent media. The authors found that while IL-8 and VEGF were present in highest concentrations in conditioned media, PDGF was present in maximal amounts in spent media.
Read More...