Cancer is often caused by improper function of a few proteins, and sometimes it takes only a few proteins to malfunction to cause drastic changes in cells. Here the authors look at the genes that were mutated in patients with a type of pancreatic cancer to identify proteins that are important in causing cancer. They also determined which proteins currently lack effective treatment, and suggest that certain proteins (named KRAS, CDKN2A, and RBBP8) are the most important candidates for developing drugs to treat pancreatic cancer.
Read More...
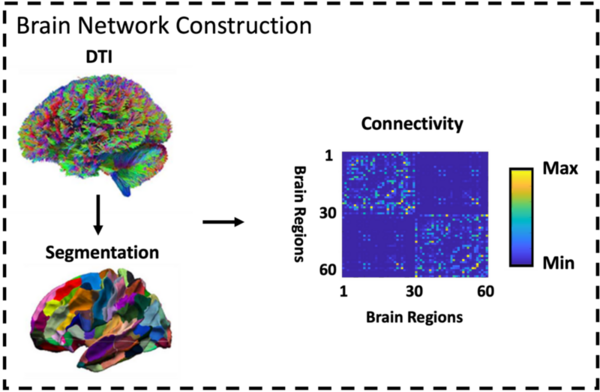
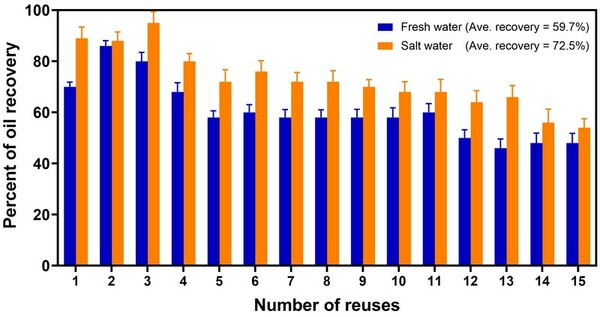
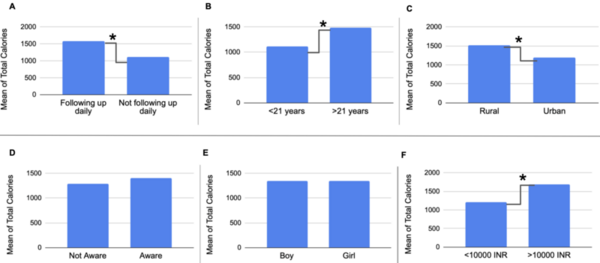




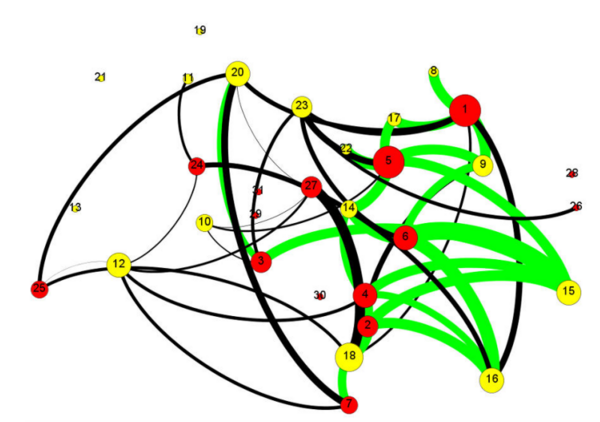
![Alterations of the [Fe/H] Values Modulate Light Curves by Absolute Magnitude in non-Blazhko RRab Lyraes](/rails/active_storage/representations/proxy/eyJfcmFpbHMiOnsibWVzc2FnZSI6IkJBaHBBallHIiwiZXhwIjpudWxsLCJwdXIiOiJibG9iX2lkIn19--7d8b84074a7b504657e6acd5ed4f66e4b84daf63/eyJfcmFpbHMiOnsibWVzc2FnZSI6IkJBaDdCem9MWm05eWJXRjBTU0lJY0c1bkJqb0dSVlE2QzNKbGMybDZaVWtpRFRZd01IZzJNREErQmpzR1ZBPT0iLCJleHAiOm51bGwsInB1ciI6InZhcmlhdGlvbiJ9fQ==--33b2b080106a274a4ca568f8742d366d42f20c14/Figure_4.png)