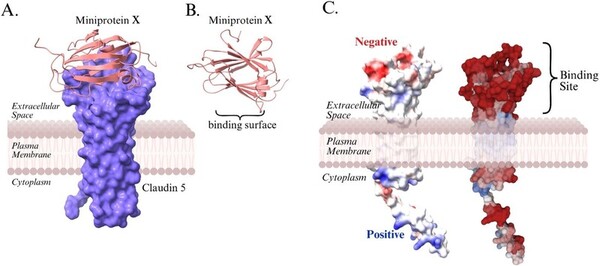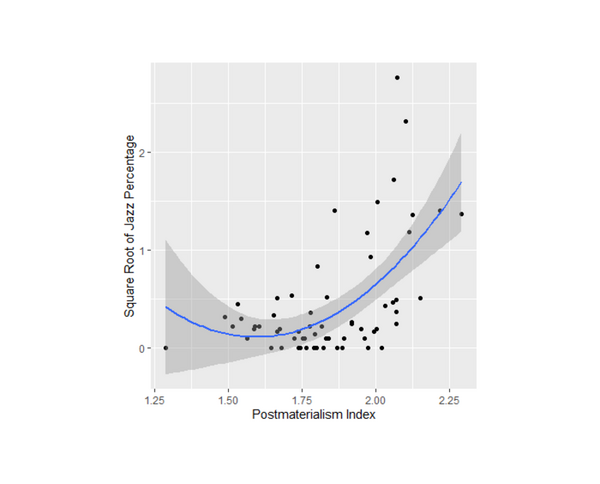
Jazz music is a unique American art form that has spread around the world. Iyer and Iyer study this spread through a computational sociology project examining how jazz popularity is correlated with postmaterialism (an ideology that values self-expression) and political activity.
Read More...