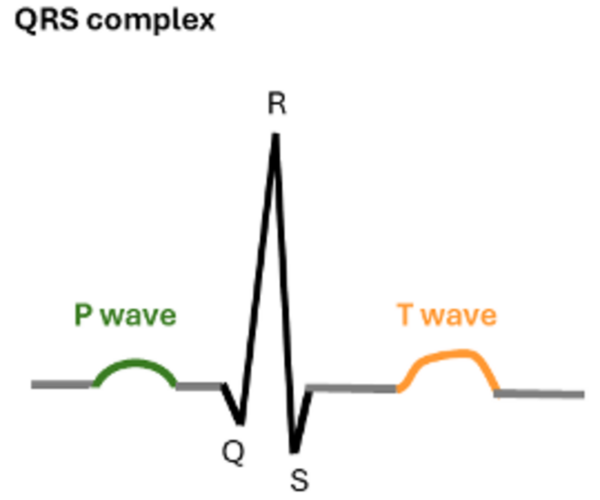
Arrhythmias vary in type and treatment, and ECGs are used to detect them, though human interpretation can be inconsistent. The researchers tested four tree-based algorithms (gradient boosting, random forest, decision tree, and extra trees) on ECG data from over 10,000 patients.
Read More...