The impact of political ideologies on renewable energy adoption
(1) Dublin High School, (2) Medtronic
https://doi.org/10.59720/23-258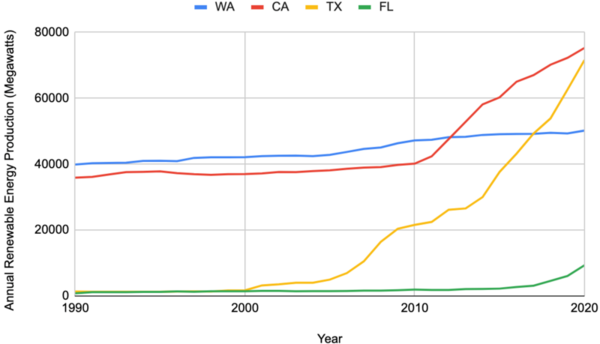
Due to the growing urgency of climate change, renewable energy technologies have become an increasingly popular source of energy. However, differing perceptions on the urgency of climate change along political party lines may result in variable rates of adoption of these renewable energy technologies. This study explores the hypothesis that Republican states are less inclined to adopt renewable energy technologies than Democratic states. To test this hypothesis, we analyzed overall renewable energy production across two Democratic states (Washington and California) and two Republican states (Texas and Florida). We investigated correlations between the energy production of each state and used t-tests to assess statistical significance. Contrary to our hypothesis, however, we concluded that there was no observable correlation between political ideologies and renewable energy adoption. In fact, Texas, a Republican state, showed the fastest renewable energy production growth rate and produced the most wind energy compared to California, Washington, and Florida. Our findings suggested that factors beyond party lines likely influence state-level decisions regarding renewable energy sources. Understanding these factors is critical to create policies to combat climate change and drive renewable energy adoption worldwide.
This article has been tagged with: