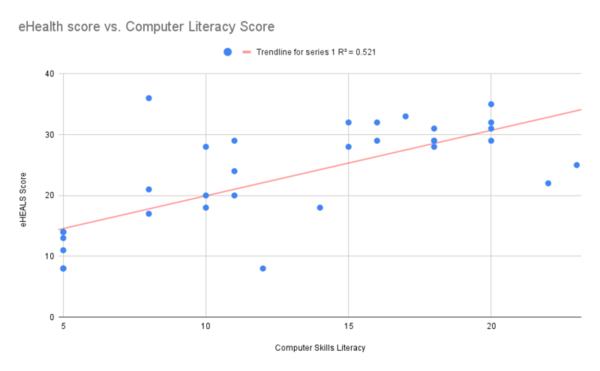
Many cases of viral hepatitis are easily preventable if caught early; however, a lack of public awareness regarding often leads to diagnoses near the final stages of disease when it is most lethal. Thus, we wanted to understand to what extent an individual's sex, age, education and country of residence (India or Singapore) impacts disease identification. We sent out a survey and quiz to residents in India (n = 239) and Singapore (n = 130) with questions that test their knowledge and awareness of the disease. We hypothesized that older and more educated individuals would score higher because they are more experienced, but that the Indian population will not be as knowledgeable as the Singaporean population because they do not have as many resources, such as socioeconomic access to schools and accessibility to healthcare, available to them. Additionally, we predicted that there would not be any notable differences between make and females. The results revealed that the accuracy for all groups we looked at was primarily below 50%, demonstrating a severe knowledge gap. Therefore, we concluded that if more medical professionals discussed viral hepatitis during hospital visits and in schools, patients can avoid the end stages of the disease in notable cases.
Read More...