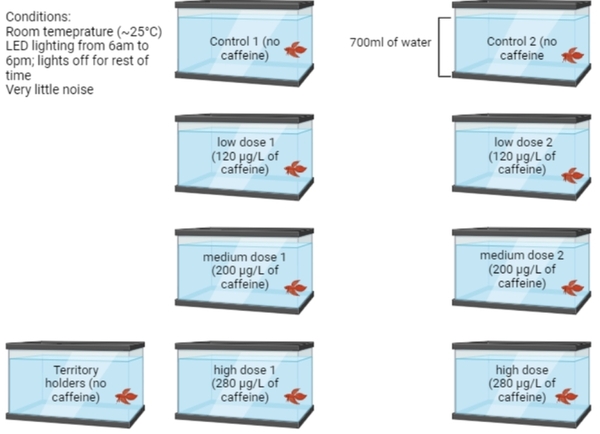
In this article the authors looked at the effect of spending time with a therapy dog before and after stressful events. They found that interacting with a therapy before a stressful event showed more significant reduction in signs of stress compared to interacting with a therapy dog after stressful events have already occurred.
Read More...