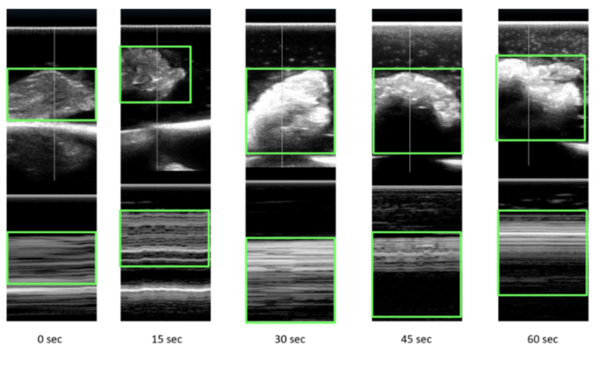
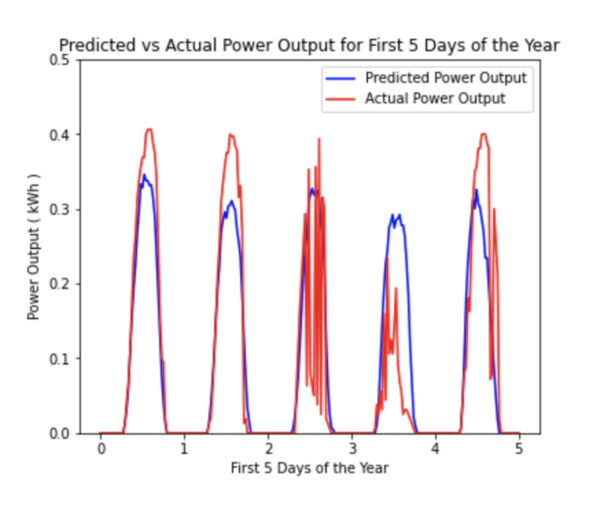
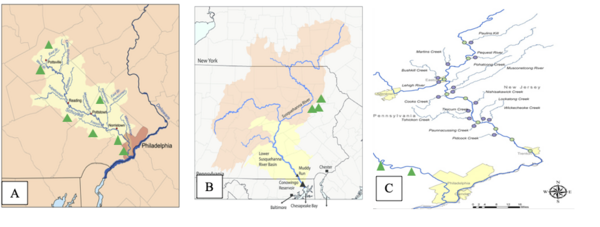
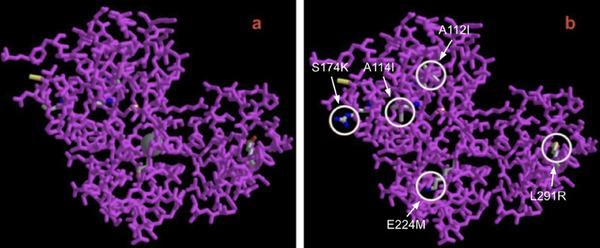
Seeking an approach to address the increasing levels of methane and chlorinated hydrocarbons that threaten the environment, the authors worked to develop a novel, low-cost biotrickling filter for use as an ex situ method tailored to marine environments. By using methanotrophic bacteria in the filter, they observed methane degradation, suggesting the feasibility of chlorinated hydrocarbon degradation.
Read More...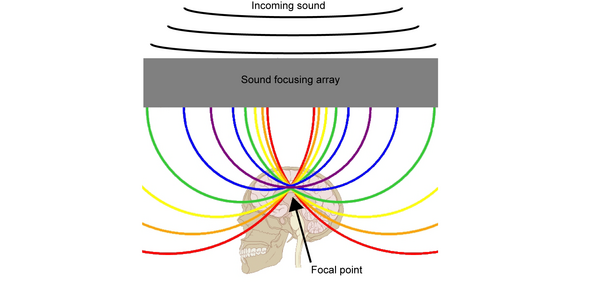
.png)