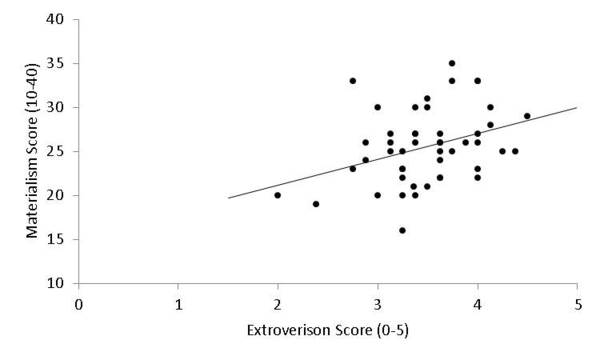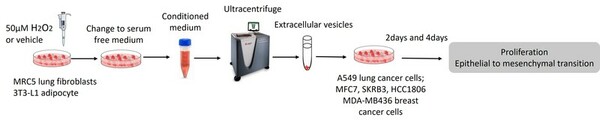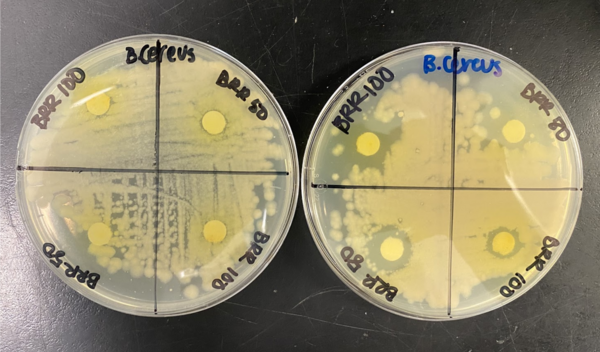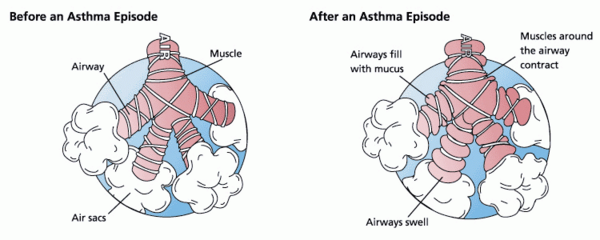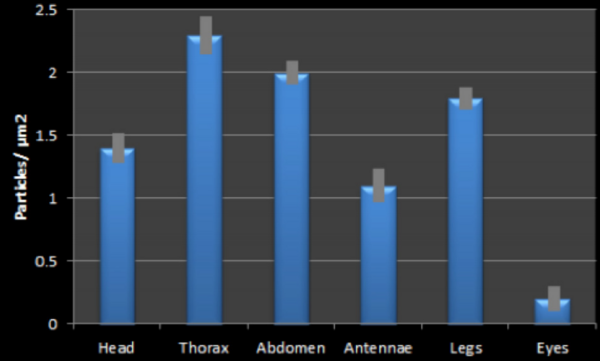
The cause of insect colony collapse disorder (CCD) is still a mystery. In this study, the authors aimed to test the effects of two environmental factors, water vapor and smoke levels, on the social behavior and physical condition of insects. Their findings could help shed light on how changing environmental factors can contribute to CCD.
Read More...