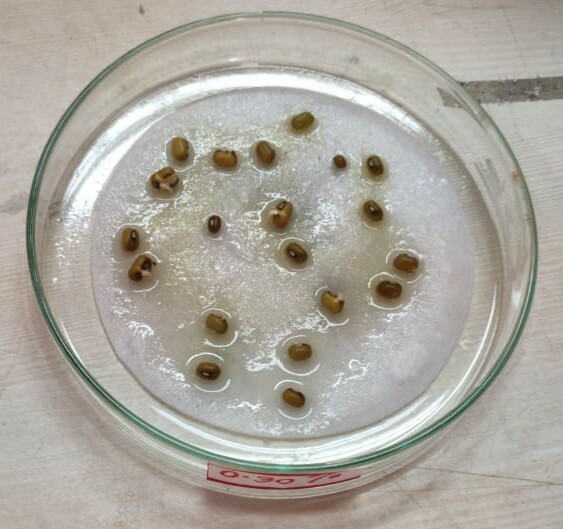
Ethinyl estradiol and progestin norgestrel are commonly present in contraceptive tablets and it is unknown how they affect the environment. In this study, the authors investigate the role that ethinyl estradiol and progestin norgestrel have on the growth of flowering plants. The percentage germination, embryonic and adventitious tissue proliferation, root length, and shoot length were measured in V. radiata and T. aestivum treated with each compound and results demonstrate that ethinyl estradiol and progestin norgestrel can induce growth in both plants at certain concentrations. These findings have important implications as societal use of chemicals increases and more make their way into the environment.
Read More...