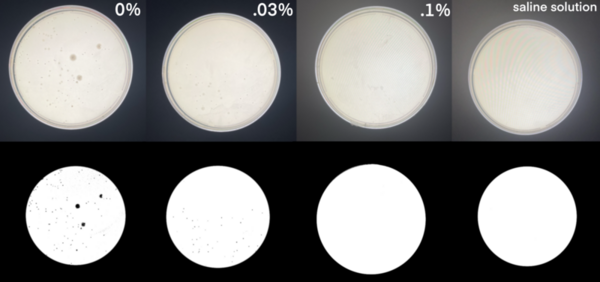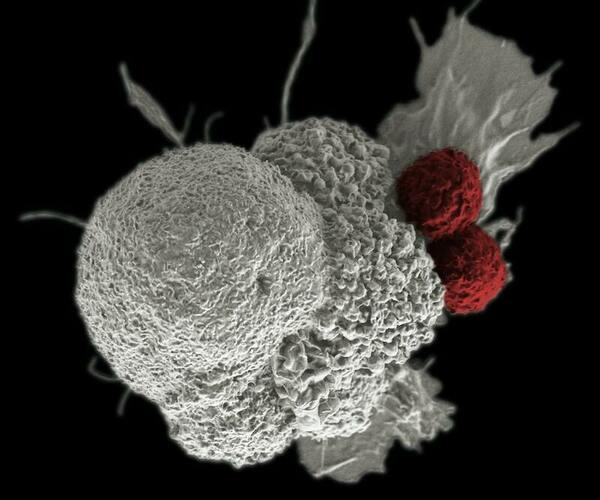
Since cancer cells inhibit T-cell activity, the authors investigated a method to reverse T-cell disfunction with gene therapy, so that the T-cells would become effective once again in fighting cancer cells. They used the inhibition of proprotein convertases (PCSK1) in T cells and programmed death-ligand 1 (CD274) in cancer cells. They observed the recovery of IL-2 expression in Jurkat cells, with increased recovery noted in a co-culture sample. This study suggests a novel strategy to reactivate T cells.
Read More...