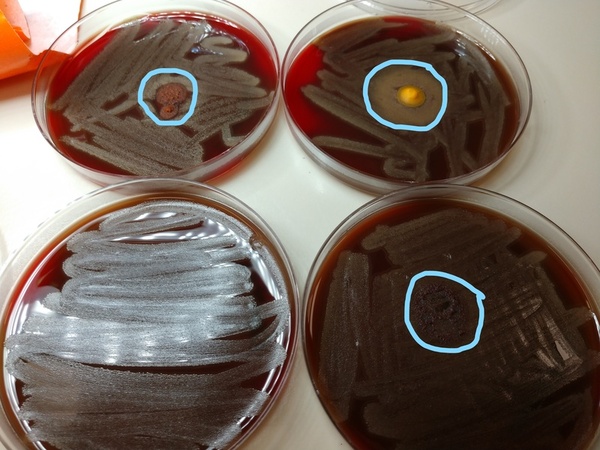
The authors experimented with several commonly available alkaline spices (turmeric, cayenne pepper, and cinnamon) to study their antimicrobial properties, hypothesizing that alkaline spices would have antimicrobial activity. Results showed a zone of inhibition of bacterial growth, with the largest zone of inhibition being around turmeric, followed by cayenne pepper, and the smallest around cinnamon. These results are impactful, as common alkaline spices generally do show antibacterial properties and both bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects correlated with degree of alkalinity.
Read More...