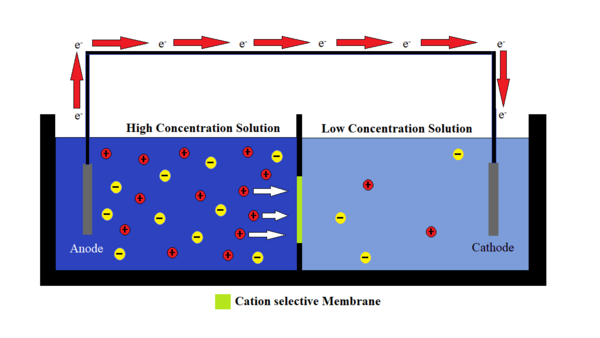
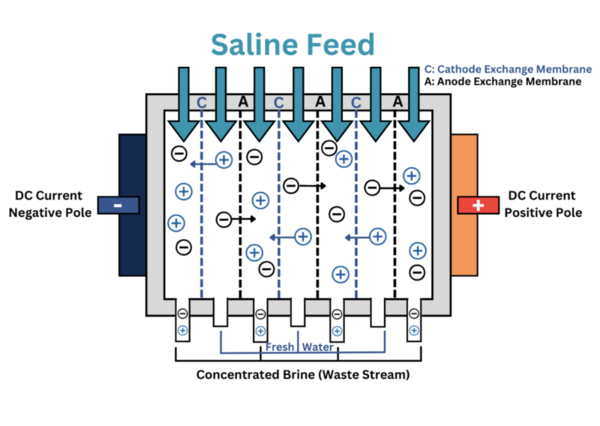
One largely untapped source of clean energy is the use of osmotic gradients where freshwater and saltwater are mixed, for example at estuaries. To harness such energy, charge-selective membranes are needed to separate the anions and cations in saltwater, establishing an electric potential like a battery. The objective of this study was twofold: to investigate the creation of the polymer matrix and test the properties of boron nitride nanotubes, as both are essential in the creation of an ion-selective membrane. Out of three polymer samples tested in this study, the mixture known as Soltech 704 showed the best resistance to etching, as well as the highest UV cure rate.
Read More...


.PNG)