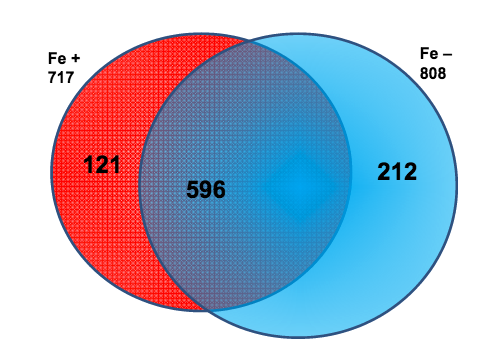
Although the United States maintains millions of square kilometers of nature reserves to protect the biodiversity of the specimens living there, little is known about how confining these species within designated protected lands influences the genetic variation required for a healthy population. In this study, the authors sequenced genetic barcodes of insects from a recently established nature reserve, the Southwestern Riverside County Multi-Species Reserve (SWRCMSR), and a non-protected area, the Mt. San Jacinto College (MSJC) Menifee campus, to compare the genetic variation between the two populations. Their results demonstrated that the midge fly population from the SWRCMSR had fewer unique DNA barcode sequence changes than the MSJC population, indicating that the comparatively younger nature reserve's population had likely not yet established its own unique genetic drift changes.
Read More...