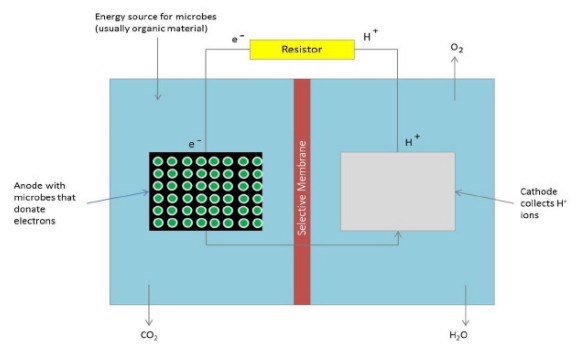
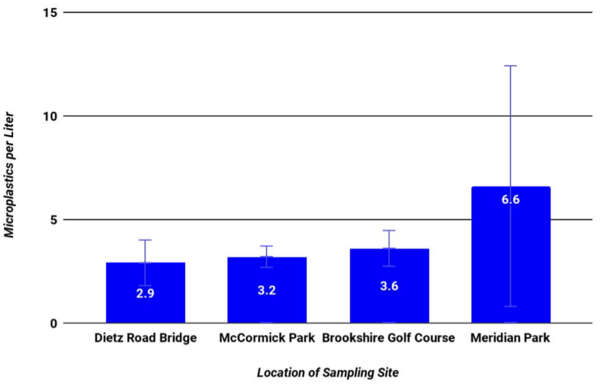
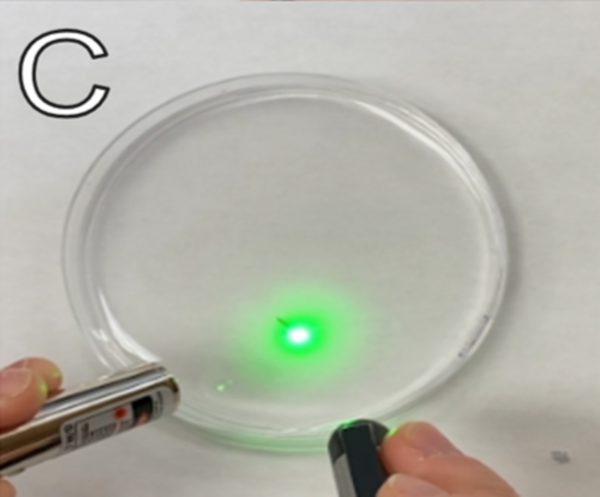
Heliobacter felis causes gastritis which is accompanied by a range of unpleasant symptoms in small animals such as cats. In order to identify effective antibiotics for treating H. felis infections, the researchers investigate whether a combination of different antibiotics is more effective than the use of individual antibiotics alone. Of the antibiotics they selected, Streptomycin alone was better than any other single antibiotic or in combination. Their results have not yet been validated in live animals, but suggest that Streptomycin alone might be an effective treatment of H. felis-induced gastritis in cats.
Read More...