Stress and anxiety have become more prevalent issues in recent years with teenagers especially at risk. Recent studies show that experiencing stress while learning can impair brain-cell communication thus negatively impacting learning. Green tea is believed to have the opposite effect, aiding in learning and memory retention. In this study, the authors used Lymnaea stagnalis , a pond snail, to explore the relationship between green tea and a stressor that impairs memory formation to determine the effects of both green tea and stress on the snails’ ability to learn, form, and retain memories. Using a conditioned taste aversion (CTA) assay, where snails are exposed to a sweet substance followed by a bitter taste with the number of biting responses being recorded, the authors found that stress was shown to be harmful to snail learning and memory for short-term, intermediate, and long-term memory.
Read More...Browse Articles
Improving Wound Healing by Breaking Down Biofilm Formation and Reducing Nosocomial Infections
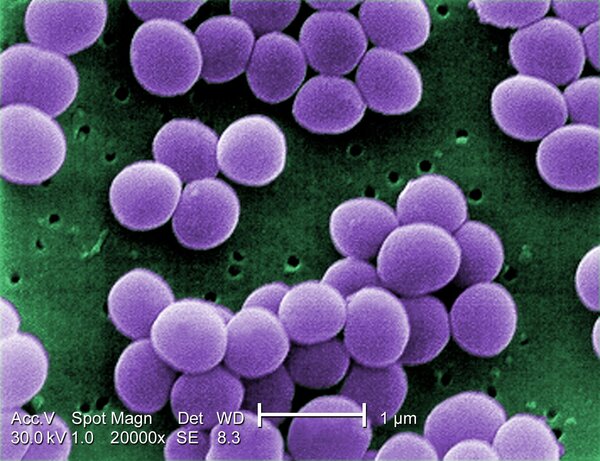
In a 10-year period in the early 2000’s, hospital-based (nosocomial) infections increased by 123%, and this number is increasing as time goes on. The purpose of this experiment was to use hyaluronic acid, silver nanoparticles, and a bacteriophage cocktail to create a hydrogel that promotes wound healing by increasing cell proliferation while simultaneously disrupting biofilm formation and breaking down Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which are two strains of bacteria that attribute to nosocomial infections and are increasing in antibiotic resistance.
Read More...The Cohesiveness of the Oscillating Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction
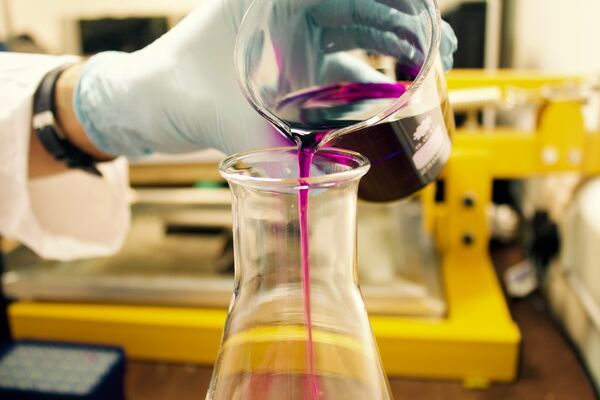

In this study the author undertakes a careful characterization of a special type of chemical reaction, called an oscillating Belousov-Zhabotinsky (or B-Z) reaction, which has a number of existing applications in biomedical engineering as well as the potential to be useful in future developments in other fields of science and engineering. Specifically, she uses experimental measurements in combination with computational analysis to investigate whether the reaction is cohesive – that is, whether the oscillations between chemical states will remain consistent or change over time as the reaction progresses. Her results indicate that the reaction is not cohesive, providing an important foundation for the development of future technologies using B-Z reactions.
Read More...Application of gene therapy for reversing T-cell dysfunction in cancer
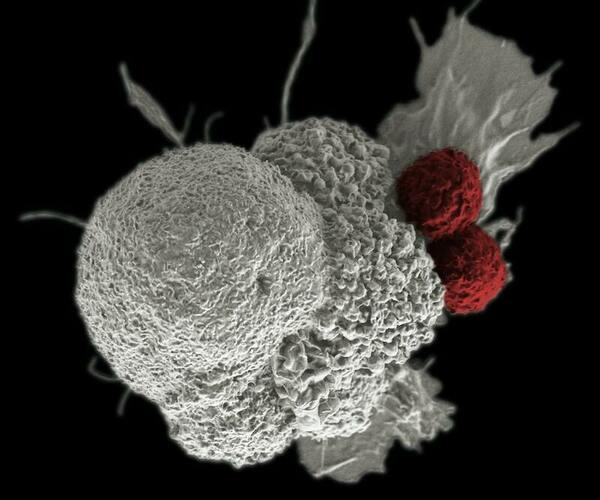
Since cancer cells inhibit T-cell activity, the authors investigated a method to reverse T-cell disfunction with gene therapy, so that the T-cells would become effective once again in fighting cancer cells. They used the inhibition of proprotein convertases (PCSK1) in T cells and programmed death-ligand 1 (CD274) in cancer cells. They observed the recovery of IL-2 expression in Jurkat cells, with increased recovery noted in a co-culture sample. This study suggests a novel strategy to reactivate T cells.
Read More...In vitro Comparison of Anticancer and Immunomodulatory Activities of Resveratrol and its Oligomers
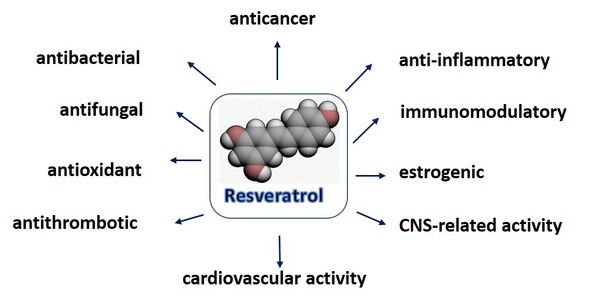
Resveratrol is a type of stillbenoid, a phenolic compound produced in plants, that is known for its anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects. Many oligomers of resveratrol have recently been isolated their bioactivities remain unknown. Here, authors compared the bioactivities of resveratrol with natural dimers (ε-viniferin and gnetin H) and trimers (suffruticosol B and C). Results provide preliminary evidence that resveratrol oligomers could be potential preventive or therapeutic agents for cancers and other immune-related diseases
Read More...Star anise and oregano essential oil: A comparative evaluation of antibacterial effect
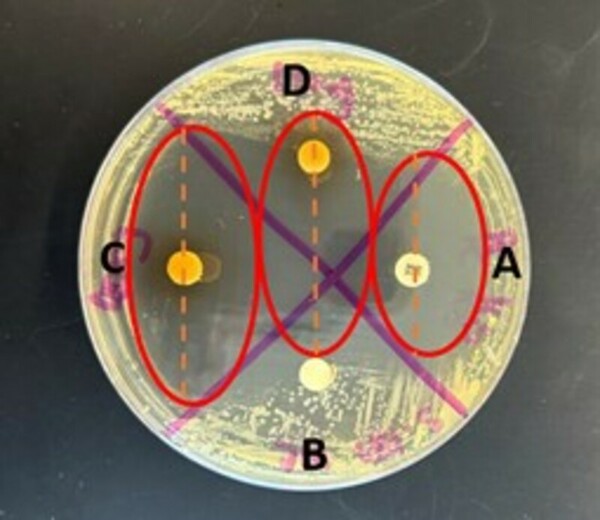
The authors looked at the antibacterial effects of oregano and star anise essential oils against E. coli or S. epidermis. They found that oregano oil showed antibacterial activity against both E. coli or S. epidermis, and that star anise oil had a larger zone of inhibition in E. coli than tetracycline, a conventional antibiotic.
Read More...The influence of music on lexical decision-making in adolescents

The lexical decision task is designed to test aspects of vocabulary retrieval from short-term and long-term memory by prompting the subject to differentiate between words and non-words. From this task, researchers can determine the effects of certain stimuli on linguistic processing. Numerous studies have investigated the effects of music on various cognitive capacities, like memory and vocabulary. In the current study, we hypothesized that participants would show greater accuracy rates on the lexical decision task when exposed to a selected piece of classical music while completing the task, as compared to completing the task in silence. We tested this hypothesis on a group of 25 participants who completed the lexical decision task once in silence and once while listening to Beethoven's “Moonlight Sonata, 1st Movement”. The results suggest a positive association between the effects of classical background music and improved accuracy. Our results indicate that listening to certain types of music may enhance linguistic processes such as reading and writing. Further research with a larger group of participants is necessary to better understand the association between music and linguistic processing abilities.
Read More...Reduce the harm of acid rain to plants by producing nitrogen fertilizer through neutralization

The phenomenon of dying trees and plants in areas affected by acid rain has become increasingly problematic in recent times. Is there any method to efficiently utilize the rainwater and reduce the harmfulness of acid rain or make it beneficial to plants? This study aimed to investigate the potential of neutralizing acid rainwater infiltrating the soil to increase soil pH, produce beneficial salts for plants, and support better plant growth. To test this hypothesis, precipitation samples were collected from six states in the U.S. in 2022, and the pH of the acid rain was measured to obtain a representative pH value for the country. Experiments were then conducted to simulate the neutralization of acid rain and the subsequent change in soil pH levels. To evaluate the effectiveness and feasibility of this method, cat grass was planted in pots of soil soaked with solutions mimicking acid rain, with control and experimental groups receiving neutralizing agents (ammonium hydroxide) or not. Plant growth was measured by analyzing the height of the plants. Results demonstrated that neutralizing agents were effective in improving soil pH levels and that the resulting salts produced were beneficial to the growth of the grass. The findings suggest that this method could be applied on a larger agricultural scale to reduce the harmful effects of acid rain and increase agricultural efficiency.
Read More...Music's Effect on Dogs' Heart Rates
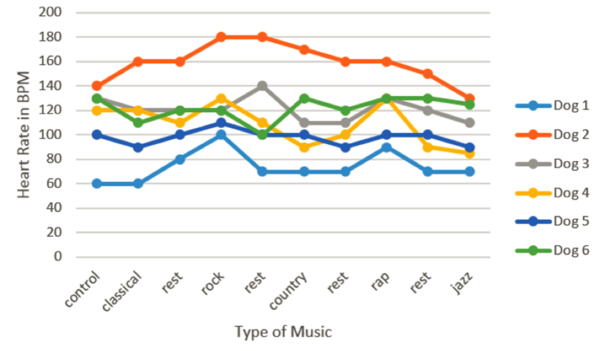
Music can affect the behavior of humans and other animals. In this study, the authors studied five types of music with different tempos and demonstrated how each one affected dogs' heart rates.
Read More...Effect of Collagen Gel Structure on Fibroblast Phenotype
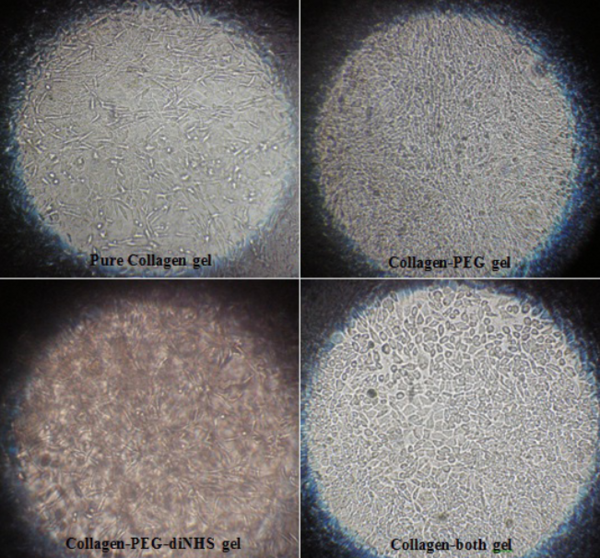
Environment affects the progression of life, especially at the cellular level. This study investigates multiple 3-dimensional growth environments, also known as scaffolds or hydrogels, and their effect on the growth of a type of cells called fibroblasts. These results suggest that a scaffold made of collagen and polyethylene glycol are favorable for cell growth. This research is useful for developing implantable devices to aid wound healing.
Read More...Search Articles
Search articles by title, author name, or tags