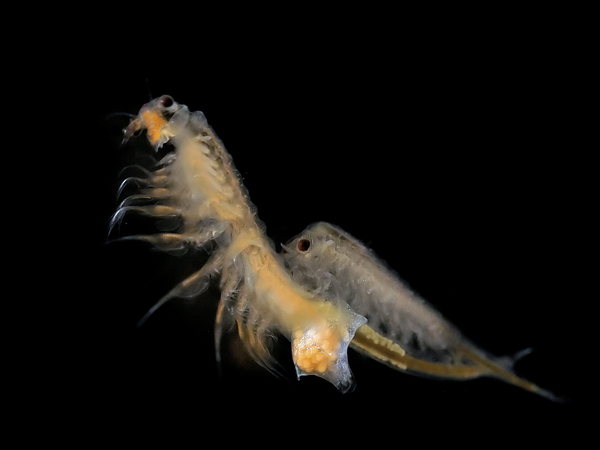
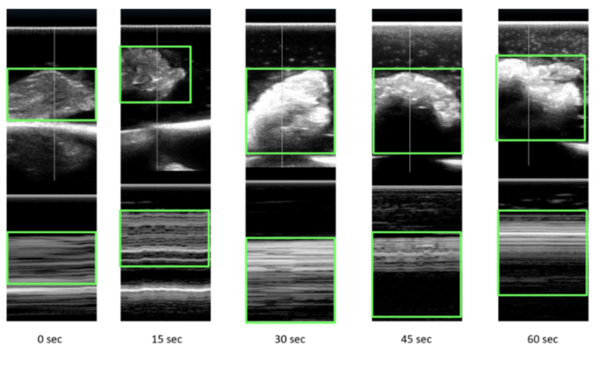
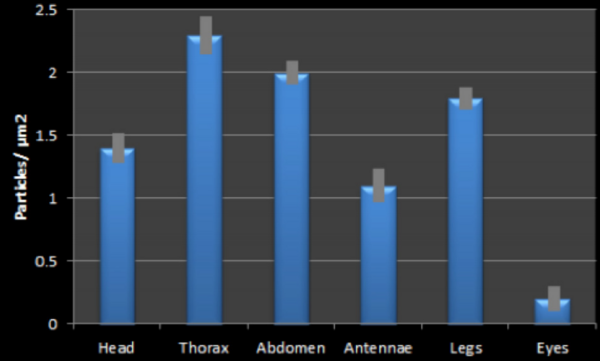
Cannabidiol, or CBD, is a widely available over the counter treatment used for various medical conditions. However, CBD exerts its effects on the endocannabinoid system, which is involved in neural maturation, and could potentially have adverse effects on brain development. Here, the impact of CBD on the development of brine shrimp (Artemia salina) was assessed. Differences in dose responses were observed.
Read More...


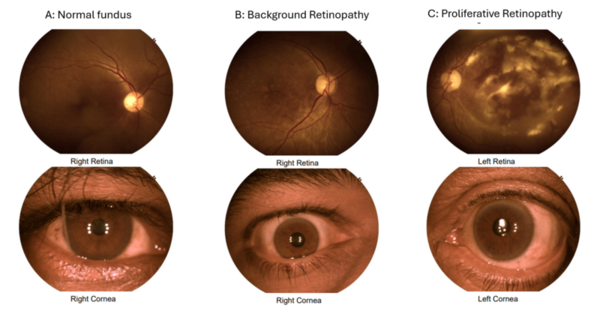
.png)