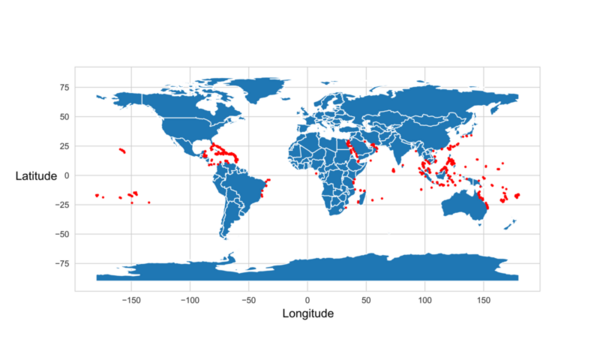
Coral bleaching is a fatal process that reduces coral diversity, leads to habitat loss for marine organisms, and is a symptom of climate change. This process occurs when corals expel their symbiotic dinoflagellates, algae that photosynthesize within coral tissue providing corals with glucose. Restoration efforts have attempted to repair damaged reefs; however, there are over 360,000 square miles of coral reefs worldwide, making it challenging to target conservation efforts. Thus, predicting the likelihood of bleaching in a certain region would make it easier to allocate resources for conservation efforts. We developed a machine learning model to predict global locations at risk for coral bleaching. Data obtained from the Biological and Chemical Oceanography Data Management Office consisted of various coral bleaching events and the parameters under which the bleaching occurred. Sea surface temperature, sea surface temperature anomalies, longitude, latitude, and coral depth below the surface were the features found to be most correlated to coral bleaching. Thirty-nine machine learning models were tested to determine which one most accurately used the parameters of interest to predict the percentage of corals that would be bleached. A random forest regressor model with an R-squared value of 0.25 and a root mean squared error value of 7.91 was determined to be the best model for predicting coral bleaching. In the end, the random model had a 96% accuracy in predicting the percentage of corals that would be bleached. This prediction system can make it easier for researchers and conservationists to identify coral bleaching hotspots and properly allocate resources to prevent or mitigate bleaching events.
Read More...