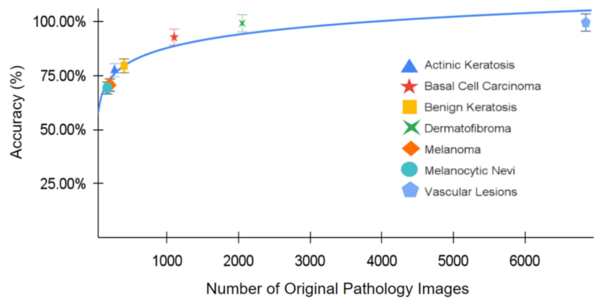
In this study, the authors developed and assessed the accuracy of a machine learning algorithm to identify skin cancers using images of biopsies.
Read More...A novel CNN-based machine learning approach to identify skin cancers

In this study, the authors developed and assessed the accuracy of a machine learning algorithm to identify skin cancers using images of biopsies.
Read More...Effect of environmental factors on bacterial flora of normal human skin
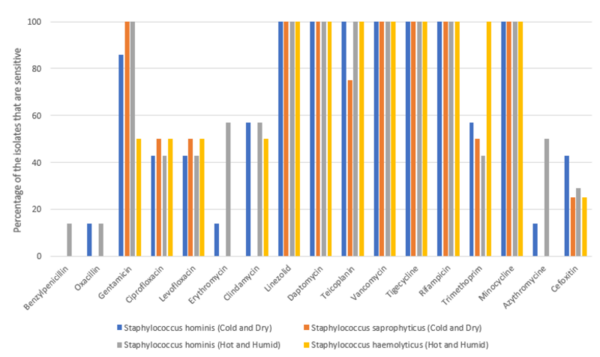
The authors looked how different working conditions impacted the microbiome of the human skin.
Read More...Reduced psoriasis skin irritation symptoms through the effects of Chinese herbal medicines on planarians
The authors looked at whether traditional Chinese medicine remedies that target the lungs and liver would reduce inflammation in a planaria model. They found that the two active compounds they tested were able to decrease induced inflammation by 97-98%.
Read More...Characterization of Inflammatory Cytokine Gene Expression in a Family with a History of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a heritable autoimmune disorder characterized by abnormal red and itchy skin patches. The authors study the family of a man with psoriasis. They explore whether the man's children, who do not show any symptoms of psoriasis, demonstrate gene expression consistent with the disease.
Read More...Preliminary investigation of Allosauroidea facial integument and the evolution of theropod facial armor
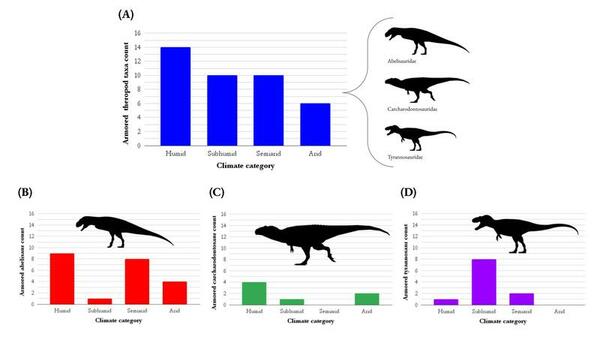
The facial integument, or external skin tissues, were assessed on set of dinosaurs from the Allosauroidea clade to test whether dermal patterns served specific functions.
Read More...Cutibacterium acnes sequence space topology implicates recA and guaA as potential virulence factors
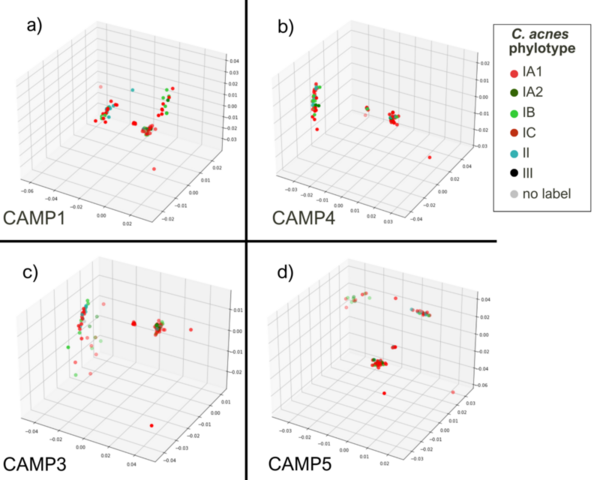
Cutibacterium acnes is a bacterium believed to play an important role in the pathogenesis of common skin diseases such as acne vulgaris. Currently, acne is known to be associated with strains from the type IA1 and IC clades of C. acnes, while those from the type IA2, IB, II, and III phylogroups are associated with skin health. This is the first study to explore the sequence space of individual gene products of different C. acnes phylogroups. Our analysis compared the sequence space topology of virulence factors to proteins with unknown functions and housekeeping proteins. We hypothesized that sequence space features of virulence factors are different from housekeeping protein features, which potentially provides an avenue to deduce unknown proteins’ functions. This proposition should be confirmed based on further experimental outcomes. A notable similarity in the sequence spaces’ topological features of previously known as housekeeping proteins encoded by recA and guaA genes to ‘putative virulence’ genes camp2 and tly was observed. Our research suggests further investigation of recA and guaA’s potential virulence properties to better understand acne pathogenesis and develop more targeted acne treatments.
Read More...Entropy-based subset selection principal component analysis for diabetes risk factor identification
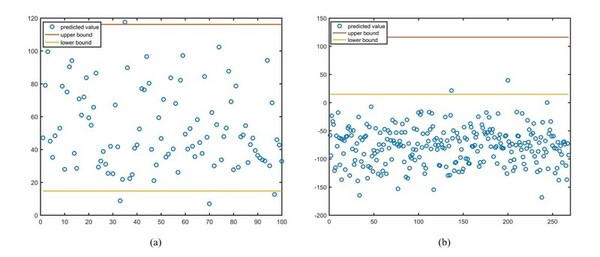
In this article, the authors looked at developing a strategy that would allow for earlier diagnosis of Diabetes as that improves long-term outcomes. They were able to find that BMI, tricep skin fold thickness, and blood pressure are the risk factors with the highest accuracy in predicting diabetes risk.
Read More...Refinement of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Atopic Dermatitis related Filaggrin through R packages

In the United States, there are currently 17.8 million affected by atopic dermatitis (AD), commonly known as eczema. It is characterized by itching and skin inflammation. AD patients are at higher risk for infections, depression, cancer, and suicide. Genetics, environment, and stress are some of the causes of the disease. With the rise of personalized medicine and the acceptance of gene-editing technologies, AD-related variations need to be identified for treatment. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have associated the Filaggrin (FLG) gene with AD but have not identified specific problematic single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). This research aimed to refine known SNPs of FLG for gene editing technologies to establish a causal link between specific SNPs and the diseases and to target the polymorphisms. The research utilized R and its Bioconductor packages to refine data from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's (NCBI's) Variation Viewer. The algorithm filtered the dataset by coding regions and conserved domains. The algorithm also removed synonymous variations and treated non-synonymous, frameshift, and nonsense separately. The non-synonymous variations were refined and ordered by the BLOSUM62 substitution matrix. Overall, the analysis removed 96.65% of data, which was redundant or not the focus of the research and ordered the remaining relevant data by impact. The code for the project can also be repurposed as a tool for other diseases. The research can help solve GWAS's imprecise identification challenge. This research is the first step in providing the refined databases required for gene-editing treatment.
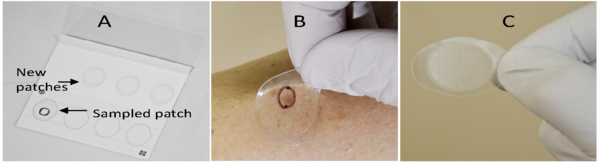
Read More...Durability of the Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) Patch Adhesive
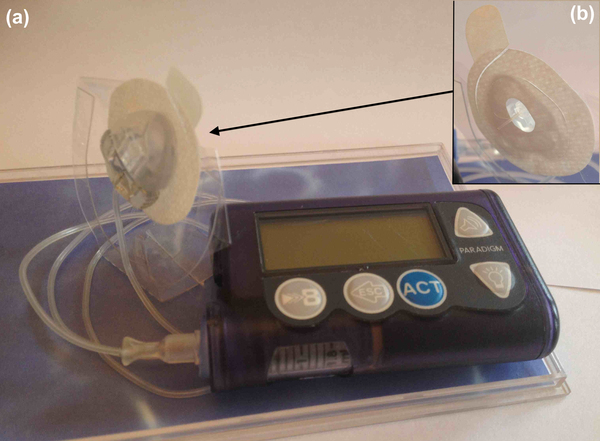
Insulin infusion patches are a common way for diabetics to receive medication. The durability of two different patch adhesives was compared on artificial skin with and without artificial sweat.
Read More...Exploring natural ways to maintain keratin production in hair follicles
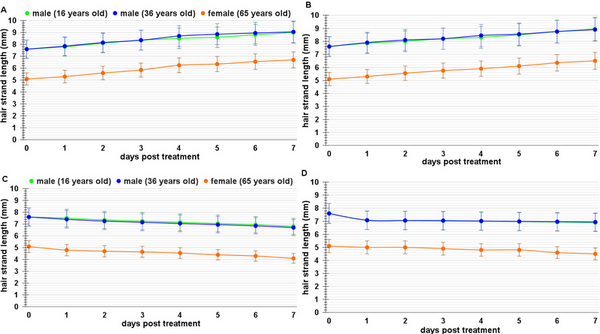
We are looking into natural ways to help hair grow better and stronger by studying keratin synthesis in human hair follicles. The reason for conducting this research was to have the ability to control hair growth through future innovations. We wanted to answer the question: How can we find natural ways to enhance hair growth by understanding the connection with natural resources, particularly keratin dynamics? The main focus of this experiment is understanding the promotion of keratin synthesis within human hair follicles, which is important for hair development and health. While keratin is essential for the growth and strength of body tissues, including skin and hair, our research hints at its specific synthesis within hair follicles. In our research utilizing castor oil, coconut oil, a turmeric and baking soda mixture, and a sugar, honey, and lemon mixture, we hypothesize that oils, specifically coconut oil and castor oil, will enhance keratin synthesis, whereas mixtures, such as the turmeric and baking soda mixture and the sugar, honey, and lemon mixture, will result in a decrease keratin synthesis. The methods used show how different natural substances influence keratin formation within the hair follicles. The experiment involved applying natural resources to hair strands and follicles, measuring their length under the microscope daily, and assessing their health and characteristics over seven days. In summary, our research helps us understand how hair grows better. We found that using natural items like essential oils effectively alters keratin growth within the hair follicles and hair strands.
Read More...