In this paper, Thomas et al. introduce a new, affordable way to study characteristics of rocket motors using small-scale rocket motors.
Read More...Browse Articles
Differential privacy in machine learning for traffic forecasting
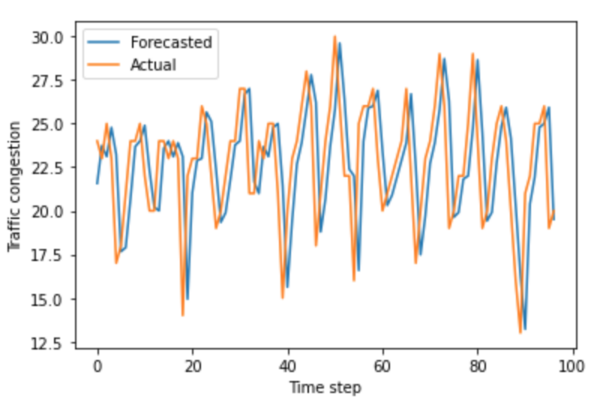
In this paper, we measured the privacy budgets and utilities of different differentially private mechanisms combined with different machine learning models that forecast traffic congestion at future timestamps. We expected the ANNs combined with the Staircase mechanism to perform the best with every value in the privacy budget range, especially with the medium high values of the privacy budget. In this study, we used the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) and neural network models to forecast and then added differentially private Laplacian, Gaussian, and Staircase noise to our datasets. We tested two real traffic congestion datasets, experimented with the different models, and examined their utility for different privacy budgets. We found that a favorable combination for this application was neural networks with the Staircase mechanism. Our findings identify the optimal models when dealing with tricky time series forecasting and can be used in non-traffic applications like disease tracking and population growth.
Read More...Artificial Intelligence Networks Towards Learning Without Forgetting

In their paper, Kreiman et al. examined what it takes for an artificial neural network to be able to perform well on a new task without forgetting its previous knowledge. By comparing methods that stop task forgetting, they found that longer training times and maintenance of the most important connections in a particular task while training on a new one helped the neural network maintain its performance on both tasks. The authors hope that this proof-of-principle research will someday contribute to artificial intelligence that better mimics natural human intelligence.
Read More...The most efficient position of magnets

Here, the authors investigated the most efficient way to position magnets to hold the most pieces of paper on the surface of a refrigerator. They used a regression model along with an artificial neural network to identify the most efficient positions of four magnets to be at the vertices of a rectangle.
Read More...String analysis of exon 10 of the CFTR gene and the use of Bioinformatics in determination of the most accurate DNA indicator for CF prediction
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease caused by mutations in the CFTR gene. In this paper, the authors attempt to identify variations in stretches of up to 8 nucleotides in the protein-coding portions of the CFTR gene that are associated with disease development. This would allow screening of newborns or even fetuses in utero to determine the likelihood they develop cystic fibrosis.
Read More...Reading recall: A comparison of reading comprehension

Researchers query whether reading comprehension is the same, worse, or better when using e-books as compared with standard paper texts. This study evaluated this question in the elementary school population. Our hypothesis was that information would be retained equally whether read from paper or from an electronic device. Each participant read four stories, alternating between electronic and paper media types. After each reading, the participants completed a five-question test covering the information read. The study participants correctly answered 167 out of 200 comprehension questions when reading from an electronic device. These same participants correctly answered 145 out of 200 comprehension questions when reading from paper. At a significance level of p < 0.05, the results showed that there was a statistically significant difference in reading comprehension between the two media, demonstrating better comprehension when using electronic media. The unexpected results of this study demonstrate a shift in children’s performance and desirability of using electronic media as a reading source.
Read More...An improved video fingerprinting attack on users of the Tor network
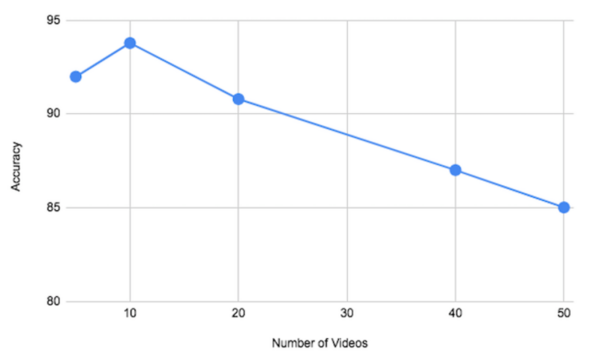
The Tor network allows individuals to secure their online identities by encrypting their traffic, however it is vulnerable to fingerprinting attacks that threaten users' online privacy. In this paper, the authors develop a new video fingerprinting model to explore how well video streaming can be fingerprinted in Tor. They found that their model could distinguish which one of 50 videos a user was hypothetically watching on the Tor network with 85% accuracy, demonstrating that video fingerprinting is a serious threat to the privacy of Tor users.
Read More...The Role of a Mask - Understanding the Performance of Deep Neural Networks to Detect, Segment, and Extract Cellular Nuclei from Microscopy Images
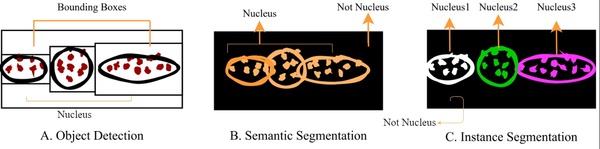
Cell segmentation is the task of identifying cell nuclei instances in fluorescence microscopy images. The goal of this paper is to benchmark the performance of representative deep learning techniques for cell nuclei segmentation using standard datasets and common evaluation criteria. This research establishes an important baseline for cell nuclei segmentation, enabling researchers to continually refine and deploy neural models for real-world clinical applications.
Read More...The effect of floating plant on water purification: Comparison of the water purification capability of Water Hyacinth, Duckweed, and Azolla

Clean water is a necessity for every household, yet water pollution is a serious problem in many parts of the world and plays a major role in compromising water security in the 21st century. In this paper, the authors address the utility of several plants as natural water purifiers. They estimate the effectiveness of duckweed, hyacinth, and azolla in improving the quality of water from the Mithi river in India by measuring several metrics. They conclude that all three plants are effective in improving water quality, suggesting that these plants as eco-friendly options for water treatment.
Read More...A Taste of Sweetness in Bioplastics

Sweet potatoes are one of the most common starches in Taiwan, and sweet potato peels hold significant potential to make biodegradable plastics which can alleviate the environmental impact of conventional petroleum-based plastics. In this paper, Tsai et al created starch-based bioplastics derived from sweet potato peels and manipulated the amount of added glycerol to alter the plastic’s strength and flexibility properties. Their results indicated that higher concentrations of glycerol yield more malleable plastics, providing insights into how recycled agricultural waste material might be used to slow down the rate of pollution caused by widespread production of conventional plastics.
Read More...