Testing Various Synthetic and Natural Fiber Materials for Soundproofing
(1) Dhahran British Grammar School, Dhahran, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, (2) Prince Mohammad bin Fahd University, Khobar, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
https://doi.org/10.59720/16-099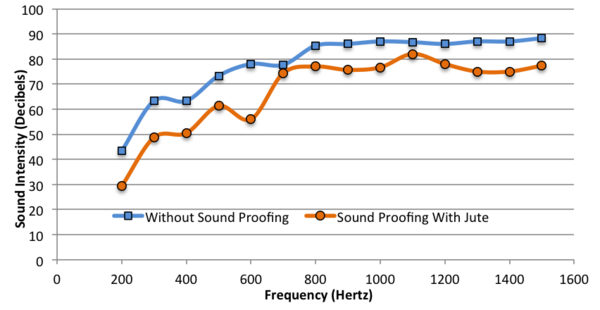
Noise pollution negatively impacts the health and behavioral routines of humans and other animals. Excessive sound vibrations in urbanized settings can also cause structural damage, leading to property devaluation. The increased use of electrical and mechanical appliances at home has further created a concern for noise pollution, and the production of synthetic sound-absorbing materials contributes to harmful gas emissions into the atmosphere. The goal of this study is to assess environmentally-friendly, cheap natural-fiber materials, such as jute, as an effective replacement for synthetic materials, such as gypsum and foam. The selected materials are used widely in other industries but no direct comparison has been performed to evaluate which materials are best at absorbing sound. Our results indicate that among the synthetic and fiber materials, jute fiber is the best performer: jute with a thickness of 1 cm absorbed a sound intensity of 51 dB at 400 Hz, which was 21.12% more efficient than no soundproofing and 12.57% more efficient than gypsum. These results provide a significant breakthrough in soundproofing. Low cost fiber materials can be used for reducing sounds of televisions, computers, and appliances at home, or in broadcast studios for audio recordings. Other natural fiber materials should also be investigated for their soundproofing abilities in future studies.
This article has been tagged with: